Category: Digital Transformation
If you are planning to select Business Intelligence (BI) tool for your Big Data solutions, it is important to evaluate which one is the best suited and not best rated for your company. Selecting a right visualization tool that can help you get the most out of Big Data and has well-defined functions, is an important criterion of the process. So you should ask the following questions before selecting the best tool for your company.
1. What are you visualizing?
It is important to first understand why you are looking for the tool in the first place. If you are planning to visualize the internal data such as marketing, finance, etc. you should look for a tool that is in alignment with your management system. For example, if you are using SAP ECC/Net Weaver system for handling internal data, an SAP-based BI will work better for easy implementation and cost reduction on training. Similarly, if you are going to use the tool for a client, it is better to use something that is compatible with what your client is using.
2. How is the tool’s interface?
It is imperative that the tool has an easy to use Graphical User Interface (GUI). Tools are meant to save time and make the task easy. A well-designed tool that offers access to various options can be put in the pipeline with ease. Check if it has nice graphics capabilities in case you need to visualize decision trees and so on.
3. Does it have the essential support for visual discovery?
Tools should provide the most basic support for visual discovery and query processing. This might include something as simple as comma-separated values file, text, Excel, and XML support. Apart from these basic things, you might need to check what programming language it supports. Your decision will rest on what your internal team is expert at handling. Your team can get to support for various well-known programming languages such as C++, Python, Java, and Perl.
The other thing to check is whether or not the visualization tool you are planning to use is compatible with the operating system you use. In case of cloud implementation, ask the cloud provider for an OS that is compatible with your visualization tool. If you are catering to a client, ensure that the OS you select is compatible with their systems too.
4. Is the price right?
It is no surprise that price plays an important role in finalizing a lot of things in any company. BI projects cost a lot and the cost will largely depend on a number of criteria such as the level of in-house expertise and the ultimate goal to be achieved. Visualization tools should not be judged on the basis of their price alone but compared with how big is the need and what is being provided.
A good way to make a decision is to try a free trial version of the software to check whether it works for you or not. The tool provider should offer good technical support along with the documentation that covers all aspects of the tool.
5. How flexible is the tool?
Big Data is evolving at a phenomenal rate and so is the technology around it. Make sure that the visualization tool that you are seeking is flexible enough to adapt to these changes. Ask the provider how easy it is to upgrade the tool so that you do not hit a roadblock and require a complete overhaul in the near future.
Understanding these points will help you start zeroing on a list of visualization tools but seeking the support of an experienced tool provider will help you finalize it. Look for someone like us who have an expertise in understanding the requirements of the client and providing a complete solution.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
If your company is dealing with Big Data, Data analytics and visualization is a must-have tool to understand and gain insights effectively. There are several tools available in this sector that promise to convert raw data and produce it as solutions that are easily understandable. These solutions can be in the form of charts, videos, infographics or even highly engaging and intuitive presentation that uses Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality (VR & AR). Here are the top 7 data analytics and visualization tools that you can hire to get the most out of your data.
1. Tableau
Tableau is one of the most widely used data visualization software due to its user-friendly, intuitive design, and excellent official supporting documentation. This data analytics and visualization tool are available in five different versions – Desktop, Server, Online, Mobile, and free-to-use Tableau Public. It has the capacity to produce interactive visualizations that are compatible with huge and very fast-changing data sets used in Big Data operations involving artificial intelligence and machine learning applications. It is designed to work great with almost all advanced database solutions such as Hadoop, Amazon AWS, My SQL, SAP, and Teradata.
2. Sisense
This tool is smartly designed to provide a full stack analytics platform with ease of use. The interface offers users a chance to simply drag and drop charts and more complex graphics for achieving interactive visualizations without much of a hassle. The tool has the capability to gather data from multiple sources and query them instantaneously along with an option to share the dashboard across organizations. Sisense is a powerful tool for people who are experienced in this field and can be a little overwhelming for newcomers.
3. Plotly
Plotly is a web-based data visualization platform that lets the user create simple to complex charts directly inside their web browser. It offers a clean, intuitive and fully-featured interface for free, but its commercial package provides more user-friendliness and support. Its ability to enable more complex and sophisticated visualization is a direct result of integration with analytics related programming languages such as R, Python, and Matlab.
4. FusionCharts
This Javascript-based data analytics and visualization tool has the ability to produce 90 different chart types and integrates a large number of platforms and frameworks to offer optimum flexibility. It is one of the leaders in the paid-for market simply because it offers many live templates where users can simply plug in their data instead of starting one from scratch.
5. Google Charts
Google is at the forefront of technology and it stays the course by providing an entire set of data visualization tools that support various data formats including geolocation and offers a variety of outputs. But keep in mind that Google Charts are for people who have worked with data before and can code in JavaScript to make the best use of this amazing tool.
6. QlikView
QlikView tool is a major vendor that competes for supremacy with Tableau since it also provides a wide feature range and high customization setup. It does take time to get used to it, but can be very powerful when used to its full potential. There are numerous third-party resources available online for this clean and clutter-free tool. It additionally offers powerful business intelligence, analytics, and enterprise reporting.
7. Datawrapper
Datawrapper is the perfect tool for media organizations that are looking for creating simple charts to present statistics. It’s simple and clean interface allows easy CSV data upload, to create simple charts and maps that can be quickly embedded into reports.
Data analytics and visualization tools are abundantly available and seeking the best one for your organization can be difficult. It is better to seek the expertise of consultants such as our organization to get the most out of your Big Data.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
In today’s age of hyper-competition, businesses need to focus their systems on the customer. A critical area of focus is business software. Much of business software hitherto focused on internal efficiency. However, competitive pressure mandate a realign, with the focus on the customer, and specifically customer support.
Businesses Need to Roll Out Mobile Solutions
Nowadays, the basic support for customer commerce is through customer-facing mobile apps. About 80% of shoppers use their mobile phones for product reviews, to compare prices, and find store locations. A good chunk of these customers completes the purchase process online as well. About 54% of Millennials and 49% of Non-Millennials prefer shopping online. Businesses need to roll out customer-facing mobile apps and responsive websites, to facilitate e-commerce and other customer interactions.
The Rise of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
E-commerce websites offer a world of convenience to the customer. It brings the shopping experience anywhere, from home to office, and from the boardroom to the bathroom. However, such convenience comes without the “touch-and-feel” experience of physical stores. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (VTR) technologies bridge the shortcoming and offer the best of both worlds.
Cases of retailers supporting customer commerce through VR and AR-based software abound.
- Swedish furniture giant IKEA’s VR app allows customers to view different kitchen decors. Customers can walk around IKEA kitchens virtually, using a VR headset and app.
- Sephora’s app allows users to take selfies and apply the brand’s cosmetic products to their images. Customers can get conclusive proof of whether a shade of lipstick will look good on them, rather than debate endlessly or speculate.
Artificial Intelligence Systems Facilitate Personalization
Personalization is the order of the day.
Most businesses already use Google Analytics tool to segment customers. They target segmented groups with different discounts and deals. Marketers also use various other predictive analytics tools to analyze historical data. Advanced solutions deliver accurate predictions about demand. Enterprises could focus their efforts on products having the greatest potential for profits.
However, such a superficial approach will undergo a sea-change by 2018. More-and-more shoppers now leverage Artificial Intelligence, to source products, bargain prices, and pick up products. As a case in point, connected smart fridges detect when the stock of milk becomes low, and trigger an automatic reorder with a linked e-commerce store. Enterprises who can roll out business software to align with such smart systems, and leverage “A-Commerce” or Artificial Intelligence-based commerce, stands to gain big.
Adaptive Design Comes Centrestage
Customers’ needs are never set in stone. Smart businesses keep track of changing customer preferences and the underlying influencers of such change. Business software which connects with potential clients on a personal level, in real-time, is central to such efforts.
Use-cases abound for businesses leveraging technology, to adapting its products and services to serve real-time customer needs.
- Curve, a credit card company allows customers to switch cards even after completing the purchase. An executive purchasing a computer for the company with his personal card, to take advantage of a bargain, could later change the billing to the company card, after getting authorization.
- KLM’s new clip, attached to the traveler’s bag, offers real-time directions, suggestions, and alternatives. For instance, when a user is stuck in a long line at the Eiffel Tower, the clip suggests the nearby hot-air balloon at Parc André Citroën. The clip also directs users to specific in-house services, stealing customers away from the competition.
- Tesla recently increased the range of its electric vehicles for customers struck in places affected by Hurricane Irma. Range limitations in Tesla’s vehicles meant owners couldn’t evacuate the area.
Virtual Companions Become Mainstream
Most smart businesses now empower their workforce, especially support agents with virtual assistants. Such virtual assistants automate daily tasks in ways CRM can never enable.
Virtual assistants offer agents deep real-time insights on information hidden inside the company databases and other systems. Locating such information manually is a time-consuming task, in the absence of clear-cut information on where such information resides. The obvious benefit is a speedier resolution of consumer issues, leading to improved customer satisfaction and accelerated sales cycles.
Virtual assistants also take the shape of chatbots, replacing the manual assistant altogether. Technology has evolved considerably on this front, and businesses are co-opting it in a big way. In 2018, even the most basic bots will become more interactive than Siri and Alexia of today.
AI infused bots learn from users, to offer highly relevant insight and suggestions. It could open the database and pry a solution even before a manual agent has the chance to comprehend the question. Further, the technology to make bots understand emotional intelligence has arrived. Such Emotional Intelligence capable bots would know how exactly to respond to a frustrated customer. Going forward, bots would handle most normal queries, leaving human agents only with long-tail and complicated queries.
Social Media Rises in Importance
Social media caught on big-time, with estimates suggesting a 394% increase in social media use in recent years. The widespread popularity is mainly on account of the transparency, the social media delivers. The best businesses leverage such transparency to further their business model.
Traditionally, businesses had complete control over their products and services. The business model essentially boiled down to a “take-it-or-leave-it” approach. The transparency infused by social media has changed the power equations. Customers now have unprecedented choice and ability to gather real feedback from real users of any product or service. If something goes wrong, rest assured everyone will come to know about it.
Smart companies cope with such change by giving more power to its customers. They listen to the customer eagerly and align their business software to take feedback. This ensures that the business and the customer work together, for mutual benefit. Businesses roll out more collaborative systems and link it to their key product development and management channels.
Enterprises need not always go in search of new technologies. What is important is the way in which any technology, new or old is applied. Any business today needs to adapt and change its services and products to meet the changing needs of the customers. Customer focused business software is a major enabler in this direction.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The year 2017 has been eventful for digital transformation, with technologies such as Big Data coming of age. Digital transformation promises to be more disruptive in 2018, as evident from the following predictions.
1. IoT Becoming Mainstream
The much-hyped IoT will walk its talk fully in 2018. About 8.4 million “things” are already part of the IoT ecosystem, a 30% increase from last year’s levels. Enterprises will start using IoT to deliver better products, services, and insights. IoT will permeate to the masses, and become mainstream and commonplace.
Among specific sectors, IoT will revolutionize analytics in a big way, driving new smart solutions. A few possibilities include hyper-efficient fleet operations, intelligent traffic signals, and more. Tech giants such as Microsoft, IBM, SAS, and SAP are all heavily investing in IoT Analytics, offering a portent of the things to come.
2. Edge Computing Offers Effective Real-Time Processing Solution
The cloud and Big Data analytics analyze tons of data seamlessly. However, the sheer volume and velocity of data create time lag and some inefficiency. For instance, the cloud, for all its advantages, is not viable for IoT powered smart drones, autonomous vehicles, and other AI-powered smart devices. These devices need real-time and instantaneous data processing. Sending data from these devices “all the way” to the cloud is an inefficient and impractical method of processing data.
Edge computing, which performs data processing at the edge of the network, near the source of the data, promises effective solutions to the shortcomings or limitations of the cloud and big data. Edge computing, for instance, allows IoT powered devices to connect and communicate instantly and seamlessly.
Industry biggies, such as HPE and CISCO have already rolled out hardware and software to actualize Edge computing. IDC predicts 40% of all computing to happen at the edge in the next couple of years.
3. Enter the 5G Network
4G or fourth-generation wireless, synonymous with LTE (Long Term Evolution) technology, went mainstream in 2017. 5G of fifth-generation wireless will go gain ground in 2018. The need for hyper-connectivity and IoT propels the need for 5G.
The Next Generation Mobile Networks (NGMN) Alliance defines 5G as “an end-to-end ecosystem to enable a fully mobile and connected society.” 5G is not an incremental upgrade over 4G or LTE.
While the 4G focus is on raw bandwidth, 5G focuses on pervasive connectivity and super-dense network, enabling even faster and resilient access to the Internet even from the remotest caves or desolate hills. Unlike the hitherto monolith networks entities such as 2G, 3G or 4G, 5G co-opts a combination of technologies, including 2G, 3G, LTE/4G, LTE-A, Wi-Fi, and more. While emerging technologies and solutions, such as IoT, connected wearables, augmented reality and immersive gaming places a great strain on incumbent networks, 5G will run these technologies seamlessly.
Industry majors such as Sony and Samsung are investing in Gigabit LTE, the stepping stone between the incumbent LTE and 5G. The already well-entrenched Qualcomm Snapdragon technology powers Gigabit LTE. However, 5G will become a household technology only by 2020.
4. Blockchain finds Its Way
Blockchain, the secure transaction ledger system distributed across a network of computers, rather than under any single entity, will finally become mainstream by 2018. The financial industry has already started to embrace blockchain in a big way. The healthcare, entertainment, and hospitality sectors are on the verge of embracing it in a big way. Dubai is rapidly moving toward becoming the world’s first-ever blockchain-powered government by 2020.
5. Artificial Intelligence Becomes Mainstream
The market size for AI is set to double up from $2420 million in 2017 to $4066 million by 2018.
Solutions powered by Artificial Intelligence are already popular. Artificial Intelligence already powers many popular solutions, such as Alexa, Siri, Salesforce Einstein CRM, IBM Watson, SAP Leonardo, Netflix, Amazon AI, Cortana Intelligence Suite, and various customer service chatbots.
Companies will continue to roll out cutting-edge solutions based on Artificial Intelligence, especially to implement smarter and cheaper automation. The scope of artificial intelligence would expand to encompass everything from emails and content generation and from industrial manufacturing to smart grids. In fact, major companies will embed Artificial Intelligence into their core operations. Fueling the growth of Artificial Intelligence is the spread of open-source solutions. Artificial Intelligence cannot easily be integrated into closed systems.
With more investments being made betting on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Reality is losing the race significantly because Artificial Intelligence offers whatever Virtual Reality offers, in a much cheaper and better way. For instance, companies can apply 3-D visualization to train, pitch, and envision new products in a much better way than what Virtual Reality offers.
6. Anything as a Service
XaaS or “Anything as a Service” is now within the realms of possibility. The cloud-based services market now encompasses software, infrastructure, and everything else. The latest to enter the “as a service” market is a framework! Framework-as-a-Service (FaaS), which falls between SaaS and PaaS is a customizable cloud-based platform. Users may indulge in rapid prototyping, visualization, and other fast fail methods to discover whether a concept or strategy will work or not. Companies get to know the result of their initiative, without having to spend time and effort, doing it the hard way.
Side-by-side with FaaS, workplace-as-a-service (WaaS) and unified-communications-as-a-service (UaaS) will also become mainstream in 2018. Remote workplaces, powered by WaaS, will rise in a big way by 2018.
7. Low Code Platforms to Soar in Popularity
Low code development platforms (LCDP) will net a total revenue of $6.1 billion by 2018, and over $10 billion by 2019. These figures are impressive when compared with the total revenue in 2015 which was just $1.7 billion.
LCDPs allow creating apps through a configuration of functions, and intuitive drag-and-drop options, rather than by hand coding. The obvious advantage is ease of development and accelerated delivery of business applications. Acute shortage of talented programmers fuels the growth of LCDPs.
Some popular LCDPs, as of now, are Appian, Mendix, Google App maker, and Zoho Creator. The growing popularity of such low-code development platforms will spur ‘citizen development’.
Technology is always fluid. Companies who embrace the latest technology head-on to deliver better solutions for its customers stand to reap dividends. Companies who do not change will surely be swept away into obsolescence.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
What is Cognitive Computing?
Cognitive computing is the simulation of human thought processes in a computerized model, or an attempt to make computers mimic the way human brains work. Cognitive computing platforms help create automated IT systems capable of solving problems on its own, without human assistance.
Cognitive computing epitomizes a shift from programmed-systems to systems that learn and understand. Apps using cognitive computing technology feature self-learning algorithms. It makes use of techniques such as data mining, natural language processing, and pattern recognition, to acquire knowledge from the data it mines or is fed into it. The system looks for patterns and refines itself as it encounters more and more new data.
Impact of Cognitive Computing
Cognitive Computing is a disruptive technology, with major transformational impact. It has the potential to take enterprises much further than what traditional business intelligence and analytics solutions take them, manifested in several real-life use cases already widespread now.
The range of insights offered by cognitive applications extends far beyond what a traditional analytical tool provides. The process of continuous improvement and refinement makes cognitive application systems capable of anticipating new problems and modeling possible real-life solutions.The tips and recommendations get better with time, as more and more data enters its range.
Cognitive computing is already in widespread use in several artificial intelligence applications, such as robotics, virtual reality solutions, and more. Among the various sectors where the adoption is already widespread, a key area where results are already obvious is in healthcare, fitness, marketing, and sports technology.
“Coach Watson” to Set the Stage on Fire
Cognitive computing is all set to unleash big disruptions in sports technology, and change the way athletes and other stakeholders approach major sports tournaments. Leading the disruption is IBM Watson.
The versatile IBM Watson is donning a new hat, of coaching elite runners in America’s top running clubs. While there are several apps already leveraging big data to offer valuable insights and optimize an athlete’s performance, “Coach Watson” goes beyond. As it is with any typical cognitive computing application, Coach Watson pulls in data from a wide gamut of sources, analyze such information in real-time, identify trends, and deliver actionable tips to athletes, in natural language.
The following are some sources from which IBM Watson gets inputs, on the basis of which it conducts its analytics:
- Watson collects physiological and biomarker data from wearables worn by athletes.
- The system takes in the tons of unstructured data which conventional analytical tools usually fails to factor. Examples include travel schedule, the attritional effect of a long season, work and family stress, body recovery time, and more, all of which are seemingly not related but can play a critical role in an athlete’s performance
- The system pulls in latest research findings from medical journals, health and fitness history of top performers in the particular environment, and more.
- IBM has co-opted Orreco, a working partner with Oregon Track Club for six years running. Orreco provides insights on physiological test data and biomarker data and data on nutrition and sleep.
- IBM has tied up with Triax Technologies, 113 Industries, and Spare5 to enlarge the Watson ecosystem, and further deepen insights.
The insights generated by cognitive computing apps such as Watson facilitate drawing up highly customized training programs and optimizing schedules. For instance, a Cognitive computing powered app draws in data from the wearable devices, compares it to optimal body parameters, and indicate how much harder or longer to carry on with a workout, whether to lower the intensity of the workout, take a few days off to recover on encountering fatigue, how to optimize sleep schedules around travel, and several other rich insights. Such insights, hitherto not easily discernable with any authority, ensure each athlete remains in a zone of peak performance on the day of a competition and could make all the difference between a medal and an “also-ran.”
At another pane, Coach Watson works to preempt injuries, which can severely disrupt or even end an athlete’s career. For instance, continuous monitoring of biomarker data could make evident iron deficiency in the blood, offering early warning signs of an upcoming injury, weeks in advance.
Watson Powers Many Actionable Apps
Cognitive applications are in the throes of revolutionizing sports technology. Many Watson powered cognitive solutions have already hit the market, to empower coaches, trainers, players, managers, and other stakeholders in a big way.
The Triax Smart Impact Monitor (SIM), a wearable sensor embedded in headbands or skullcaps track the force and frequency of head impacts, offering proactive assistance to mitigate the situation. The device factors in diverse data sources to offer sound advice on the best course of action.
The cognitive app powering Spare 5’s Watson Golf Pro is akin to a highly resourceful personal caddy. The app accumulates a corpus of knowledge on mechanics and drills, gathered from contracted golf professionals. Amateur golfers may consult the app in natural language, and gain crucial insights related to the course, such as wind velocity, the best shots to play, and more. Seeing a golfer’s swing, the app provides feedback for improving that swing.
Cognitive Systems Lend Objectivity to Player Selection and Management
There is a big element of subjectivity in sports selection and management. Cognitive apps can offer greater insights which allow selectors, coaches, managers and other decision-makers to make informed decisions, and support their gut instincts with hard data.
For instance, cognitive computing apps can read and interpret all the press conferences made by players over the years, offering insights to selectors and managers on the mindset of the player, as in whether the player is becoming more positive, more optimistic, and other innate characteristics traits. Likewise, coaches get detailed and in-depth information about the player’s physical and mental faculties, and how they react to specific situations, allowing them to take proactive actions to manage the player well.
Cognitive apps have the capability to analyze unstructured data, meaning it can make an in-depth analysis of videos and footage of the athlete’s performance, and give real actionable recommendations. This is a big improvement from coaches and training staff watching videos, and generating pointers, manually, based on their gut instincts, and with a high degree of subjectivity and assumptions.
Cognitive Applications Enhance Fan Experience
Cognitive applications work wonders not only for athletes and the business side of sports but also for fans. A good case in point is 113 Industries “Pi” service, which has been put to good use by Pittsburgh Penguins, the famous hockey team, to analyze the huge volumes of fan-based data. The club uses such insights to develop specialized offers and services for fans, relating to concessional merchandise, pre and post game entertainment at the CONSOL Energy Center, and more.
Cognitive apps could likewise guide fans proactively, such as making explicit the train to catch to reach the stadium on time, factoring in traffic, fares, preferences, and other innate traits which the fan had to consider manually before. Cognitive apps would also guide the fan to the best parking space, without having to drive around in circles. Once inside, a cognitive app could guide the fan to the toilet with the least wait time. All these are possible in natural language.
The application of cognitive computing to enhance sports technology can deliver rich rewards across the board for all stakeholders, players, tournament organizers, coaches, spectators, fans, television broadcasters, and everyone else. However, as always, the devil lies in the details. Success depends on designing the apps right, with clarity on the objectives, and the development task done by competent and resourceful professionals who know what they are doing.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence (BI) turns data into information. It is the sum of applications, technologies, and methods adopted to glean strategically relevant information for the business. The task involves collecting, integrating, analyzing, and applying historical, current and predictive information related to the business. The objective is to gain strategic insights, evaluate risk, and improve decision-making capabilities for top management, business owners, and other stakeholders.
Business intelligence information encompasses both internal data and external data related to the business. Internal data may include operational data, data from sales, financial data, and more. External information is fairly wide in scope and may include information from the external supply chain, social media channels and more. Another dimension to external information for business intelligence is information about competitors and other companies, for benchmarking, and to gain a competitive edge over such companies.
Many businesses now apply business intelligence to make informed decisions, rather than relying on hunches or unfounded assumptions. For instance, restaurant owners use business intelligence to decide the menu to be added and removed from a restaurant menu. Automobile manufacturers apply business intelligence to add new features to their car models. Tour operators use business intelligence to optimize their itinerary. The possibilities are endless. Businesses may use Business intelligence to modify their internal work processes as well.
Business Intelligence Vs. Analytics
One might mistake Business Intelligence as being another name for the much-hackneyed business analytics. While both business intelligence and analytics involve aggregating and analyzing data, the similarity ends there.
Business intelligence aggregates data to make it explicit what is happening to the business, whereas analytics aggregate data to delve into why it happens. For instance, business intelligence evaluates sales performance by extracting data from various sources and presenting it in the form of intuitive graphs. Analytics involves running statistical tests to make explicit whether sales performance correlates with advertisements and promotions undertaken.
While both business intelligence and analytics involve analysis of data, the scope is markedly different. In a sense, Business Intelligence ends with the basic mathematical operations of addition, averages, and percentages to the dataset. Applying advanced algorithms complex formulas, statistical operations such as regression analysis, correlation analysis, and more, to answer deeper questions related to the dataset comes from the realm of analytics.
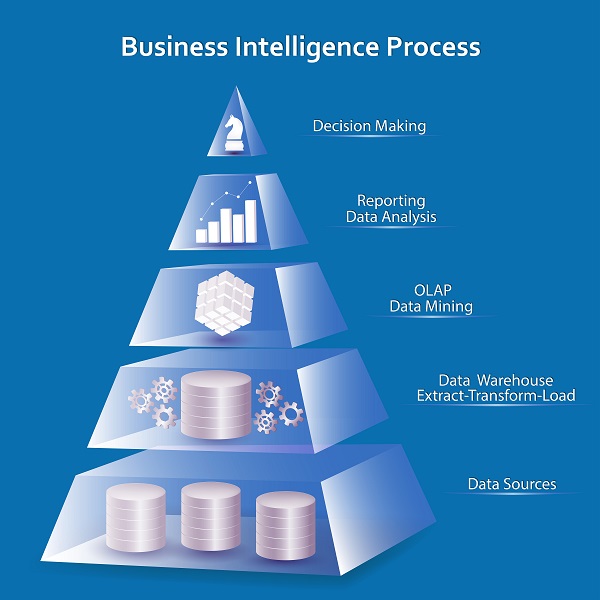
Technically, Business Intelligence encompasses ETL tools to access and transform data, OLAP (online analytical processing) tools to handle complex queries, tools to manage metadata, development tools to generate various reports and dashboards, and others tools for publishing, scheduling and distribution capabilities. Analytics co-opt different methods of analyzing information, such as descriptive, predictive, regression, neural networks, and the tools to apply such methods.
What is a Business Intelligence Software?
Business intelligence software enables enterprises to undertake business intelligence tasks.
Any Business Intelligence system worth its byte involves the following activities, and software to undertake such activity.
- Data warehousing, or bringing together all data, such as sales data, operational data, data from financial reports, competitor sales data, social media talk, and more. ETL (extract-transform-load) tools usually facilitate the task of extracting data from several databases, systems, and applications, transforming it as required, and loading it into the target data warehouses, analytical applications, and other systems.
- Data visualization, or presenting the information in a visually appealing way, for users to make sense of the data in a better way. There are different visualization types, such as charts, graphs, infographics, and more, and various enabling tools for each type. Each visualization type serves a specific purpose. For example, Pie charts are best suited to communicate relative performance, whereas bar charts depict trends in the best way. Some intuitive methods such as “slice and dice” are gaining popularity of late, for its powerful capabilities.
- Management dashboards, or well-grouped set of visualizations containing most relevant information to any stakeholders, usually reserved for top management. OLAP tools, used to aggregate data and handle complex queries, are commonly associated with Business Intelligence
Several types of tools enable data visualization and management dashboard capabilities.
- Spreadsheets such as MS-Excel are the most common method of presenting the Business Intelligence data. The ease of work nature and universal availability of spreadsheets are however marred by serious limitations, such as limited security, limited collaboration features, limited automation capabilities, and a high degree of inaccuracy and variability. Various other tools offer seamless and advanced automation, security, and audit capabilities, which MS-Excel lacks.
- Operational reports, often custom made for the enterprise, list data at a very detailed level, in a highly-structured and logical format.
- Querying and analysis solutions allow business users and analysts to generate business queries and reports rapidly. The ad-hoc nature of these tools offers unbridled flexibility. These tools also come with intuitive graphical interfaces. A middleware layer which converts database conventions to normal business nomenclature, and dashboard drag-and-drop functionality spares end-users from the need for technical proficiency to use these tools.
- Dashboard management systems offer easy access to key information in intuitive and graphical formats. It displays the required set of key performance indicators, metrics, and other relevant information in a single consolidated view, greatly improving the user’s decision-making capabilities.
- Data mining tools allow analyzing large data sets to discover patterns and build predictive models. data mining application use algorithms, statistics, advanced mathematical techniques, and sophisticated data search capabilities, to unearth insights otherwise not discoverable.
- Online analytical processing (OLAP) tools facilitate the rapid visualization and analysis of business metrics. Users may store and access data in multidimensional OLAP cubes comprising of measures, and text values. Queries from OLAP cubes are much more powerful than simple database tables and offer users advanced insights into past performance and various “what-if” scenarios. Users may use such cues to evaluate information from various dimensions and perspectives. In fact, OLAP operations constitute the fundamentals of most advanced functionality used by data visualization tools.
Top Business Intelligence Tools 2017
Until a few years ago, users had a limited choice of comprehensive Business Intelligence tools. The choice was limited to platforms offered by biggies, such as IBM, Oracle, SAP or Microsoft. The high cost of the software and the associated complexities made business intelligence out of the reach of most enterprises, except big corporations.
The advent of the cloud changed things, making business intelligence more democratic. Business no longer needed to build their own BI infrastructure in-house, as SaaS providers perform the resource-intensive tasks of data gathering, persisting and reporting, allowing businesses the ease, affordability, and convenience of the subscription model.
Some of the top ETL tools include Oracle Warehouse Builder, SAP Database Services, IBM Infosphere Information Services, SAS Data Management., Elixir Repertoire for Data ETL, SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), and more.
Some of the top OLAP tools in vogue include Yellowfin, Stratum, Birst, Profitbase BI, and the quintessential Microsoft SharePoint, among others.
Here is a rundown of some of the leading data visualization and dashboard software in 2017
- Dundas BI, one of the most popular browser-based business intelligence and data visualization platform, offers integrated dashboards, reporting tools, and data analytics capabilities.
- Domo, A cloud-based suite, makes it easy to integrate multiple data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, social media and also legacy cloud-based and on-premise solutions deployed in the enterprise.
- SiSense support business data with powerful visuals and tools, making it handy for users with little or no technical skills.
- BOARD, a centralized tool, hosts data and conducts multidimensional analyses. It boasts an impressive client list, which includes US Navy, Giorgio Armani, and Puma, among others.
- IntelliFront BI enables viewing multiple data sets from a single pane. It also distinguishes itself with strong automation features, real-time dashboards, and on-demand reporting.
Self Service Tools
The emerging trend of self-service business intelligence, made possible by the advancement of mobility, analytics, and other relevant technology, empower end-users with the ability to undertake business intelligence tasks by themselves, without necessarily having advanced technical skills.
As it is with several other sectors, Google has also entered the business intelligence space, and with time, is sure to give established incumbents a run for their money. It is now possible to build an intuitive BI dashboard powered by Google Data Studio reporting tool and Google BigQuery, a cloud-native data warehouse capable of analyzing petabytes of data in double quick time. As always, all these Google tools are open-source and free, giving developers the unbridled freedom to co-opt it in their systems, the way they want it.
Google’s new offering competes with Microsoft Power BI, another free, self-service cloud-based business intelligence offering from the Microsoft staple. Non-technical users may leverage this offering for aggregating, analyzing, visualizing and sharing data easily.
Businesses would do well to consider developing custom suites facilitating such self-service options, integrating ready-to-use Business Intelligence tools to the extent required. Partnering with a competent IT software solutions provider would enable the business to roll out highly intuitive business intelligence apps and other solutions, empowering end-users to gain the required insights easy and fast, without having to wait for the IT team to do the job and spoon-feed them with reports.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Digital transformation has turned into a ubiquitous concept that businesses can no longer afford to look away. The world is going digital at a lightning speed, making it imperative for business establishments to upgrade their skills, processes and technological know-how to this changing model. The fact that digital transformation emerged as a top concern for CIO Agenda in 2017, according to Wall Street Journal report underlines the imminence of the situation.
Leveraging digital technologies to improve business operations and organizational setups is the focus of businesses right now. If you too are considering a digital transformation initiative for your business, here are five questions to consider for making desired progress in a prioritized and strategic way:
1. Why do you need digital transformation?
‘Just because everyone is doing it’ is not the best reason to undertake a digital transformation process. It is important for an organization to understand why, if at all, they need to go through it. The best approach here is to identify the end goals you want to achieve by going digital – whether it is improving product quality, customer experiences or internal processes – and then work backward. This is particularly important for businesses, where digital processes do not directly tune in with core KPIs. Having your end goals in sight right from the onset will help you determine the outcomes of your digital transformation initiative.
2. How will you substantiate the value of your digital transformation initiative?
Well, this is one of the basic questions that must govern almost every business decision you take but is especially crucial in the case of digital transformation. You must have a clear idea as to how you plan to measure the success of your digitization plan, and for that, knowing how the concept fits into your business strategy is of paramount importance. Once these parameters have been established, the process of monitoring and gauging value of other relevant indicators, not just during the process of digital transformation but also beyond, becomes simpler. This will also save you time, effort and money in layering on technology in areas that don’t really require it.
3. Are your key stakeholders on board?
Digital transformation isn’t a small project but an extensive overhaul that will impact every single department and person associated with your business. As with every other big project, unexpected difficulties may crop up along the way. The project may get delayed or the budget may overshoot. If all your stakeholders aren’t onboard or fully convinced about the need to go digital, they may decide to pull the plug on the project. Working on your buy-in is essential to make sure all leaders and stakeholders – business partners, financiers, and shareholders – fully understand the importance of such an initiative and are committed to taking it to its logical end.
4. Have you found the right people to execute your digital transformation?
Whether you are simply revamping a website, building a new one, working on automated marketing, digitizing customer experiences, or doing it all in one go, you need the right kind of experts to get the job done and done well. Which brings up another poignant question – whether you want to hire people to do this job for you or outsource? The answer to this depends entirely on the kind of digitization you have in mind and the resources available at your disposal. If you are an established business with a long-term digital map in mind, building a core team of digital professionals is better suited. On the other hand, if you are a startup with limited resources, outsourcing may be a more practical option. Whatever your choice, you need to focus on striking that intricate balance between experience, skill and in-demand roles. There are a lot of talented professionals in the marketplace, you just need to pick the ones whose wavelength resonates with your end goals and larger KPIs.
5. Are your employees prepared for the change?
When a business undergoes a digital transformation, a lot of operational aspects are bound to change. This may mean that your employees will need to upgrade their skills and learn new processes. You cannot expect them to throw their existing work habits right out of the window and embrace the change instantaneously. A digital transformation will kick-in in the true sense only when you evolve a strategy to inform, educate and help your employees cope with the change.
Just the way every business has its own distinct identity, each digital transformation initiative is unique too. Be that as it may, these five key questions can prove vital in helping you define and execute a digital transformation that works best for your organization.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Business Consulting & Technology Augmentation delivered by Fingent helps client evolve into a regional market leader, achieve quantifiable objectives and add multiple dimensions to their business repertoire
A Top Ranking Property Management Client
A leading property investment and management company, handling more than 8000 properties segmented under single family real estate wanted to implement technological transformations to their business to soar new heights. The client manages real estate portfolios of private equity funds, offering a vertical spectrum of services ranging from property acquisition all the way to lease or sale management.

Major Roadblocks in their Real-Estate Business
Back in the day, a typical brick and mortar operational model was effective for the client, if not sophisticated. However, overhead liabilities and persistent gaps of a manual process soon curtailed scalability, and automation was inevitable.
How a Wrong Decision Curtailed Their Business
A switch was made, and a leading off-the-shelf property management software was inducted into the environment. But as is the case with most implementations, migration was far from seamless. The software primarily catered to multi-family real estate requirements, and level of customization offered was too limited. The gap was however massive, even if customizations were to be made. In the simplest terms, when the rework was exceeding the value-added work that has been budgeted for, the client realized that the project is failing. This is what happened to our client when they attempted to introduce a ready-made property management solution for their processes.
When the software fails, it jeopardizes the company’s prospects. And if the failure is large enough, it can even steal the organization’s entire future. In fact, software failures can be traced to a combination of incorrect project management, technical, and business decisions.
For every problem, there is a solution that is simple, elegant, and wrong- H. L. Mencken
The client was forced to fall back on a plethora of excel sheets to manage million dollar transactions and persist with several manual processes. They were considering alternate vendors when detailed transparent analysis and ability to comprehend the business problem firmly tilted the decision in Fingent’s direction. Following multiple rounds of promising discussions, executives at the client side were excited to begin the core transformation project with Fingent.
Finding the Right Solution

With disparate cycles amalgamating into a vertically integrated solution, a phased approach had to be adopted. The challenge was to ensure business continuity while deploying solutions on a unified platform. Business processes were classified into three major cycles – Property Acquisition, Management, and Maintenance.
- Property Acquisition – Prospective properties get channelised through an application funnel for inspection and evaluation. The value range thus assigned to a property help bidders make decisions during auctions. Acquired properties get updated on the database, and transactional parameters and contracts are abided by in the system. An assigned property manager visits respective sites, to initiate renovation and development. Three distinct mobile applications were created – for Scouting, Bidding and for the Property Manager, which are tightly integrated into the property acquisition application.
- Property Management – Application enables lease ready properties to be listed. It syndicates with several listing sites and caters to the entire lead management cycle for sales associates. All contractual formalities for leasing are taken care of within the application. An accounting module caters to the rent collection process, with a section dedicated to handling exceptions including evictions. While a mobile application caters specifically to the functionalities of a leasing agent, another app helps tenants explore the properties themselves. The latter termed the self-showing app enables physical entry into a pre-booked property view session based on geographic coordinates.
- Property Maintenance – Comprehensive property maintenance application within the real estate spectrum, enabling tenants to raise support tickets for various issues. A mobile application allows tenants to connect directly with vendors that are pre-approved and listed.
By meticulously gathering and mapping requirements, an area of expertise for the Fingent team, the project met every major milestone on time and budget. Key highlights of the comprehensive property lifecycle management include:
- Cloud-based solution delivering features via the web and mobile platform, with the capability to scale at ease. An advanced property lifecycle solution that exhaustively covers all possible process flows in single family real estate
- Seamless integration with industry leading service providers for payment, credit verification, accounting, listings etc. Individual portals for the owner, tenant, and vendor.
- Efficient data sourcing enables tight department wise integration, helps to create proficient workflow and enables easy data migration from disparate data sources. To cite an example, all parameters can be imported while acquiring a portfolio, without manual intervention
- Facilitates transparency across functions and departments alongside exhaustive customized reporting, delivering maximized performance.
The Right Software Solution can Make a Good Business Great
Deployment of a unified platform, tightly integrating all functions within the property management life cycle, transpired into exponential business growth for our client. Streamlined, end to end automated workflow meant substantial cut back on their operational overhead, while enabling phenomenal scalability.

Fingent’s client got listed by the prestigious magazine Inc., ranking amongst the Top 10 Real Estate and Top 200 overall. A whopping growth of 2626% was registered over 3 years, and company valuation increased multifold. This lead to a 1.7-Billion-dollar hedge fund investing in the client to further propel growth.
The enterprise application suite is now maturing into a comprehensive product for the real estate industry, opening up a new line of business for the client in partnership with Fingent.
To Sum Up…
The average company spends about 4-5% of revenue on IT. Much of this money goes into software and hardware, software upgrades, software license fees, and the like, but a big chunk is still for new software solutions that are assumed to create a better future for the organization and its customers. Custom software solutions and enterprise applications are now one of the largest corporate expenses outside employee costs. Yet choosing the right software vendors and getting the right solution tailored made for your processes is mission critical for every business aiming heights in today’s competitive market.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Businesses have encountered several technology waves, starting with the mainframe revolution in the 1960s to the decentralized computing wave of the 1970s, and from the advent of PCs in the 1980s to the rise of client servers in the 90s. The cloud and mobility represent the latest evolution of technology.
Such digital disruption is now a fact of life for almost all businesses. Enterprises no longer confront a question of “if,” but rather concern themselves with the “when” and “how” of digital transformation. A recent KPMG and Harvey Nash survey reveals 62% of IT professionals opine their business was already being disrupted or would be disrupted within the next two years. However, only 27% of respondents confined the presence of an enterprise-wide digital strategy.
Digital disruption is much more than co-opting new technology to the business. Businesses need to create entirely new competencies and co-opt it to incumbent legacy cultures and operating models. Here are four major questions to ask, to smooth the transformation process. These four questions also constitute a basic checklist for the digital transformation process.
1. What are the objectives of the Digital Transformation?
Embarking on a digital transformation journey is doomed to fail unless the enterprise has the end in mind, and defines a coherent strategy upfront. Implementing new technologies for the sake of it, or just because everyone else is doing so, is an exercise in futility, and may end up counterproductive by disrupting the well-entrenched ecosystem with nothing to gain in return.

Have a clear idea of the processes where digital transformation is to set in, and how the transformation would improve the process, add value, and how the intervention would make the lives of the stakeholders, from employees to customers, and from managers to owner better.
Some of the processes where digital intervention can automate the process, or make the process seamless and more accurate include form modeling, document integration, report generation, role-based accessibility and user assignment and reassignment, email notifications, task prioritization, and more. However, the possibilities are endless, limited only by imagination.
2. How much Customization will be required?

Most businesses face an issue of integration when they indulge in digital transformation, especially when the transformation involves multiple pieces of commercial software. Off the shelf software, for any function, be it operations, HR, Finance, data analytics, CRM, or any other function, will never suit enterprises perfectly. Seamless workflows will require customization as a rule.
Successful digital transformation takes place when the enterprise knows the extent of customization required. They audit the existing state, have a clear-cut idea of the desired state, have a roadmap to transform from the existing to the desired state, and map the software to the journey, to make sure the software works for the business.
A related consideration is the time-frame for the migration. A Successful digital transformation process progresses as per a predefined time frame, making sure the change does not disrupt business operations. A related challenge is slow down of operations when the new digital systems set in, owing to the learning curve. A well thought out digital transformation process factors in the delays associated with the learning curve, and pre-empt contingencies which may cause the business to screech to a grinding halt when the new software goes down to a bug.
3. How to Quantify the Value of the Digital Transformation Initiative?
Today’s businesses are driven by profits or returns on investment. The top management or owners support all change initiatives, including digital transformation initiatives based on the value it creates to the enterprise.

At the internal front, digital transformation generally makes internal processes seamless, increasing productivity and efficiency. At the customer facing end, digital transformation makes things easier for the customer, unlocks new possibilities, enable customers to buy or contact support in a much better way, and offers flexibility. However, even when the value created by the digital transformation is obvious, it still has to be quantified and made explicit. The harbingers of change need to not only know about the technologies to implement but also how to measure the value created by such initiatives. The end goal of digital transformation is to boost revenue, profitability, and investor value. Some of the factors which can be measured to link the digital transformation to such ends include inventory, human capital productivity, asset utilization, and other Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Tracking some intermediate indicators, such as sentiment and engagement is also handy.
Today, several tools make quantification easy. Nucleus Research estimates every dollar spent on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system implementation returning a whopping $8.71. Forrester’s Total Economic Impact (TEI) tool enables enterprises to quantify the potential benefits enterprises gain by implementing a stack of technologies that communicate and work together, integrated by a framework of operational transformation methodologies.
4. How to Orchestrate the Change Initiative?
Regardless of whether the initiative is a digital upgrade or digital transformation, it is essentially a change process, and change requires strong leadership.
Implementing the digital transformation requires a well-defined team with a narrow scope and a cross-functional mandate. The harbingers of digital transformation need to make a tough call on the team.

Many of the team will resist change, accustomed as they are what they have always been doing. The digital transformation initiative requires clear cut consideration on how to implement change in the least disruptive way, and chalk out strategies on how to overcome resistance to change. Training the rank and file for familiarity to the new digital processes, and factoring in a learning curve are the basic requirements, but there is also a need for clear-cut communication on why the digital transformation initiative is being carried out, and the benefits it will bring about. Most often, the digital transformation initiative will be inevitable to keep pace in the highly digitally charged world, and for the firm to stay competitive. Today’s tech-savvy customers also demand heavy digital initiatives to be satisfied.
Estimates of digital transformation failures range from 66% to 84%. It requires a method to preempt the process from descending into madness. Roping in a sound tech development partner, competent in the digital technologies you want to adopt, and backed up by the resources and talent to implement a cutting edge digital solution, is the best way to embark on a digital transformation initiative.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The transformative impact of blockchain remains much underestimated. While the concept is now associated with Bitcoins, the underlying technology could very well become the most important disruption since the arrival of Internet.
Blockchain in its purest essence is a distributed database, containing digital data. Users may access, inspect, or add to the data, but cannot change or delete it, making it tamper-proof. The original information remains as it is, leaving behind a trail, or a chain of transactions. Any single transaction would be a “block” in a never-ending chain, with the chain distributed across the internet, outside the control of anybody. Businesses leveraging block chains have an easier and safer mechanism to conduct transactions.
How Viable is Blockchain in the Supply Chain?
One area where blockchain technology is in the throes of making a big disruption is the supply chain of industries. In the existing system, the database is updated every time a movement or change takes place in the supply chain. With blockchain, every time a product changes hands, the transaction is documented, creating a permanent history of a product, from the point of origin to sale. In a traditional supply chain, each stakeholder maintains their respective records. With block chain, the records are distributed across the cyberspace, allowing for smart contracts. The distributed database runs on multiple servers, constantly checking the security and integrity of each transaction.
The application of blockchain technology in supply chain manifest in many ways:
- Real-time live recording of the quantity and transfer of assets, such as trailers, pallets, and containers
- Continuous tracking purchase orders, receipts, shipment related notifications, and other trade-related documents
- Assigning digital labels to physical goods, such as bar codes, serial numbers, RFID tags, and more. Blockchain allows connecting digital product information such as the source of origination details, batch numbers, factory and processing data, expiration dates, storage temperatures and shipping detail in a robust and inseparable way.
Improved Transparency
Blockchain brings about greater transparency in the supply chain. The log reveals the origins and touch points of each product, disseminating information on the manufacturing process, movements, and delivery, to all stakeholders. Such in-depth and finer details are not easily available now, and the potential applications of such transparency are earth-shattering:
- For perishable commodities, such as fish, blockchain records for each process, such as how and when the fish was caught or raised, whether it has been handled in a compliant manner, whether harmful formaldehyde was used in storing it, and more, increases consumer confidence and safety manifold. Walmart’s new Food Safety Collaboration Center in Beijing, where the company tied up with IBM and Tsinghua University to apply blockchain technology, to ensure food supply chain traceability and authenticity is a case in point.
- Blockchain logs make explicit the genuineness of a product, as in whether the product is really organic as claimed.
- An audit of blockchain logs make explicit whether the product was made using child labor, whether workers were paid fair wages, and whether there are any other ethically and/or legally reprehensible associations.
- Blockchain logs enhance safety. For instance, customers can track the components in their vehicle has come from an authorized manufacturer and has passed all recommended tests, increasing confidence, and reducing the risk of injury.
- In the case of defective products, the trial makes it easy to pinpoint the source of the problem and make effective amends. For instance, Blockchain production records enable tracing the place and time when a specific automobile airbags were made, allowing automakers to reduce their liability.
The trust and transparency that block chain infuses across the value chain become a new nexus for value exchange.
Security
One major impact of blockchain in the supply chain is improved security and accountability.
- The chain of logs ensures the authenticity of the product, and customers can verify the same automatically. With transactions tracked from the origin, a duplicate product or an unauthorized transaction is immediately flagged as counterfeit or theft.
- The permanent registry and verification assign tamper-proof individual identifiers to high-value products such as jewelry, making theft easily attributable. It also helps identify insurance fraud, which is a $60 billion industry in the USA.
- Blockchain serves as an escrow account, requiring all parties to confirm transactions. It eliminates the need for third parties, usually involved in the mix to ensure both parties honor their part of the contract. A shared, indelible ledger with codified rules also eliminates the need for audits.
The blockchain is on its way to enable more agile and secure value chains, with closer cooperation among stakeholders.
Process Improvements
The application of block chain in supply chain contributes greatly to process improvements.
- Blockchain logs make it very easy to detect errors or problems, and subject the supply chain movements to analytics to improve efficiency, on a dynamic basis. It also facilitates effective planning to improve processes.
- Blockchain delivers a decentralized architecture, which creates opportunities to innovate. For instance, intelligent block chain contracts query other nodes in the blockchain for the best pricing, delivery times, and other particulars. Smart shippers are already finding ways to leverage innovations to increase profits and strengthen relationships across the supply chain.
The application of blockchain technology enables tapping into rules-based intelligence, for executing business functions. Stakeholders may apply intelligent program code to embed conditions and other logic into contracts and other transactions, implemented automatically, with 100% accuracy. Manufacturers and other stakeholders can spare themselves of the copious amount of time, money, and other resources they presently spend to negotiate and communicate with other stakeholders.
The effectiveness of blockchain technology, however, depends not on blindly applying the technology per se, but developing solid and reliable apps that leverage the technology. The blockchain is only a facilitator, and it still requires cutting edge mobility solutions to power your supply chain to greater heights. Get in touch with a reliable partner for your business and mobility solutions requirements.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new