Fog Computing: The Catalyst For Efficient Data Processing
With the rise in the use of mobile phones and other smart devices, came the need for software to be ubiquitous. The amount of big data being dealt with, by enterprises across industries has also been on the rise. While we were busy wanting to access everything from everywhere, cloud computing was the technology that made it all manageable for companies and available for us.
Everyone wants to access everything from everywhere.
Cloud computing was introduced in 2000, to meet all of these demands, and provide people with ubiquitous, convenient and on-demand access to the network. It basically made use of a pool of shared configurable processing resources, such as the network and servers, that could be promptly provisioned and released with very little management efforts. The Internet of Things (IoT), also helped a great deal in keeping devices connected and enabled sharing of resources.
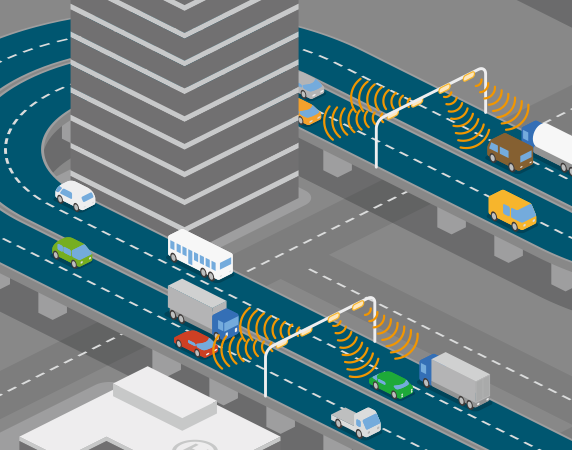
However, now we are faced with even higher levels of data, demand for flexible provisioning of resources as well as ubiquitous, on-demand access to the network. This explosion of data usage is what led to the emergence of a new, innovative computing mechanism that can provide healthy and strong real-time data analytics to clients, known as Fog Computing.
Fog computing, also known as fogging, is a kind of distributed computing system or infrastructure, in which only some of the application services are handled by the remote data centre (such as the cloud) while the rest of the services are handled at the network edge in a smart device. It is basically aimed at improving efficiencies and reducing the amount of data that is sent to the cloud for analysis, processing and storage.
While fog computing is often chosen for efficiency purposes, it can also be used for security and compliance reasons.
How it works
In a fog computing environment, most of the data processing happens in a smart mobile device, through a data hub, or on the edge of the network, through smart routers or other gateway devices.
In the normal case, a bundle of sensors generate immense volumes of data and send them to the cloud for processing and analysis. This process is not so efficient as it requires a huge bandwidth, not to mention the costs. The back-and-forth communication between the sensors and the cloud also affects the performance, leading to latency issues.
In fog computing, the analysis of data, decision-making as well as action, happen simultaneously, through IoT devices, and only the relevant data is pushed to the cloud for processing.
The architecture
A fog computing environment comprises three basic components:
- The Internet of Things (IoT) verticals or devices
- The Orchestration layer
- The Abstraction layer
All of these layers include physical as well as virtual systems that play an important role in the efficient and dynamic functioning of the fog computing system.
The IoT verticals consist of tenant applications or basically products which are rented for use. They support multi-tenancy, which enables multiple clients to host their application on a single server or a single fog computing instance. This is a very useful feature, as fog computing environments are all about flexibility and interoperability.
The orchestration layer is for data aggregation, decision making, data sharing, migration and policy management for fog computing. It consists of different APIs such as Data API and Orchestration layer API. The orchestration API holds the major analytics and intelligence services for fog computing. It also includes the policy management module, which is meant to facilitate secure sharing and communication in a distributed infrastructure.
The abstraction layer provides a uniform and programmable interface to the client. Like the cloud computing model, this layer makes use of virtualization technologies and provides generic APIs that clients can apply while creating applications to be hosted in a fog computing platform.
How does fog computing find its relevance in the real world?
Consider the example of Smart Transportation Systems (STSs). The traffic light system in a state, say, Chicago, is equipped with sensors. On an occasion of celebration, the city is likely to experience a surge of traffic around specific times, depending on the occasion. As and when the traffic starts coming in, data gets collected from the different individual traffic lights. The application that is developed by the city to monitor traffic and adjust light patterns according to timings, which runs on each edge device, automatically takes control and changes light patterns in real-time. They work according to the traffic patterns and obstructions that rise and fall, collected by the sensors. Thus, traffic is monitored flawlessly.
In the normal case, there is not much traffic data being sent to the cloud on a daily basis for analysis and processing. The relevant data here is the data that is different from the usual scenario, that is on a day of celebration or a parade. Only this data is sent to the cloud and analyzed.
Why “fog” computing
The word fog in fog computing is intended to convey the fact that cloud computing and its advantages need to be brought closer to the data source, just like the meteorological relevance of the words fog, meaning clouds that are closer to the ground.
By all means, this technological innovation is something that the world really needs now. For all those businesses who have been waiting to find the perfect solution to your data issues, fog computing is definitely the way to go.
Image credits: Quotesgram, Atelier
Stay up to date on what's new

Recommended Posts

15 Oct 2021
Data and AI: How It Has Transformed Over The Years And Trends To Watch Out For!
Undoubtedly, data is what we see almost everywhere, and it is enormous. And it doesn’t stop there, it is growing continuously at a level beyond imagination! Let’s have a look……

25 Jun 2020
What Is Fog Computing and How Does It Work?
How Can Your Business Benefit from Fog Computing? How much data do we create every day? The World Economic Forum reports that the entire digital world is expected to reach……
Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new