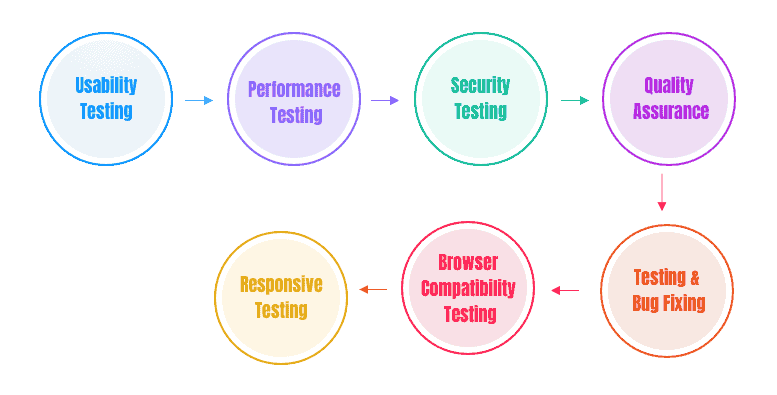
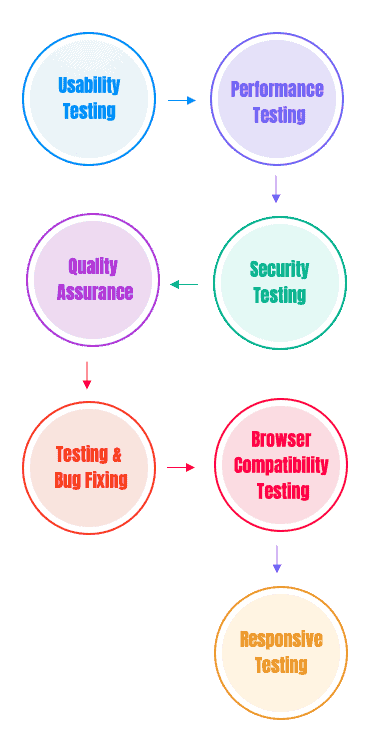
Static Web Application
Static Web Application
A static web application does not involve any interaction between the user and the server. It directly displays the content to the end user’s browser without fetching any data from the server-side. Static web apps are built using simple HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to display relevant content. In some cases, GIFs, videos, and animations are also used to attract and engage visitors. Static web apps are pretty simple and easy to manage.
A company website or a person’s portfolio website are examples of static web applications.

Dynamic Web Application
Dynamic Web Application
A web application that interacts with the client and generates real-time data based on user requests is called a dynamic web application. It includes various interactive elements and functions to engage the visitor. Dynamic web applications are substantially more complex and intricate on a technical level. A wide range of programming languages are used for building dynamic web applications, and the most common ones are PHP and ASP.NET.
An example of a dynamic web application is Facebook, where you can login easily and communicate with your friends seamlessly.

eCommerce Web Application
eCommerce Web Application
A web application in the form of a store or shop that promotes buying or selling anything online is classified as e-commerce. This web application requires some core features like electronic payment integration, transaction integration, an effective management panel for administrators (listing/updating/deleting products and managing orders/payments), and a personal cabinet for users. eCommerce apps are centered around technologies like electronic payment gateways, inventory management systems, mobile commerce, supply chain management, and the internet market.
Some popular eCommerce websites include Amazon, eBay, Walmart, Swiggy, Zomato, etc.

CMS Web Apps
CMS Web Apps
A content management system (CMS) software lets users create, manage, and modify content on a website without possessing any technical knowledge of web programming or markup languages. CMS is popular for its usage in personal blogs, corporate blogs, media sources, etc. The most commonly used content management systems are:
- WordPress: This is the most popular and trusted choice among individuals and professionals for developing a website. There are numerous plugins, themes, and online tutorials available to build unique and intuitive websites without the backup of any technical support.
- Joomla: This is an open-source CMS platform and comes next to WordPress. It comes with an intuitive interface that helps users create, manage, and modify content on a website and blogs.
- Drupal: A free CMS with an adaptable interface for building up online communities. Individuals widely use it for personal blogs, online news pages, media, corporate blogs, professional blogs, etc.

Portal Web Application
Portal Web Application
Portal web apps refer to applications that allow authenticated and authorized user access to a company’s data repository. Portals are best suited for businesses and enterprises that let users create a personal profile and include various details such as chats, emails, and forums to publish content. Only members of the portal can solely access data. Whenever a user signs in to the portal, the service provider keeps track of the user’s website activity. There are various types of web portals often associated with different industries.
Education Portals, Student Portals, Employee Portals, Banking Portals, Patient Portals, etc., are examples of portal web apps.

Single-Page Application
Single-Page Application
Single Page Application or SPA is a dynamic application that empowers visitors to communicate within a browser with no hindrances at a pace. User requests and responses occur effectively and faster than conventional web applications because SPA executes logic on the internet browser rather than the server. The SPAs are relatively simple and easy to build and debug while deploying.
For instance, while browsing your email app, the headers and sidebars stay intact while accessing your inbox. Most social network sites, email services, online video/audio players benefit swiftly from single web applications and agility. Gmail, Paypal, Netflix, Twitter, Google Maps, etc., implement single-page applications.

Multi-Page Application
Multi-Page Application
Multi-page applications or MPAs consist of multiple pages and reload the entire page from the server whenever a user navigates to a different page. MPAs are built using different languages such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, AJAX, jQuery, etc. These applications are worthwhile for their scalability with no page limits and provide vast information about company products or services.
Examples of MPA s include catalogs, web portals, business web applications, and online stores.

Rich-Internet Web Applications
Rich-Internet Web Applications
Rich Internet Applications is an application with many of the same features and appearances as a desktop application. It primarily has a lot of functionalities and is more engaging and faster than standard web-based applications. They rely upon customer-side plugins because of their browser limitations. These applications are built using tools like AJAX, Java, JavaFX, Adobe Flash, Adobe Flex and can be used offline as well. Rich-internet web apps are visually appealing and provide a great user experience.
Google docs, Youtube, Google maps are popular examples of rich-internet web applications.

Progressive Web Apps
Progressive Web Apps
Progressive web applications (PWA) are the most popular and well-developed types of web applications that look similar to mobile applications. They are also known as cross-platform web applications, which use the latest browser APIs and progressive enhancement methods to offer a native mobile app experience. The primary goal of PWA is to enhance the speed and versatility of web applications in the face of slow internet connections.
Some notable examples of progressive web applications are MakeMyTrip, Forbes, OLX, Starbucks.

 Static Web Application
Static Web Application Dynamic Web Application
Dynamic Web Application eCommerce Web Application
eCommerce Web Application CMS Web Apps
CMS Web Apps Portal Web Application
Portal Web Application Single-Page Application
Single-Page Application Multi-Page Application
Multi-Page Application Rich-Internet Web Applications
Rich-Internet Web Applications Progressive Web Apps
Progressive Web Apps