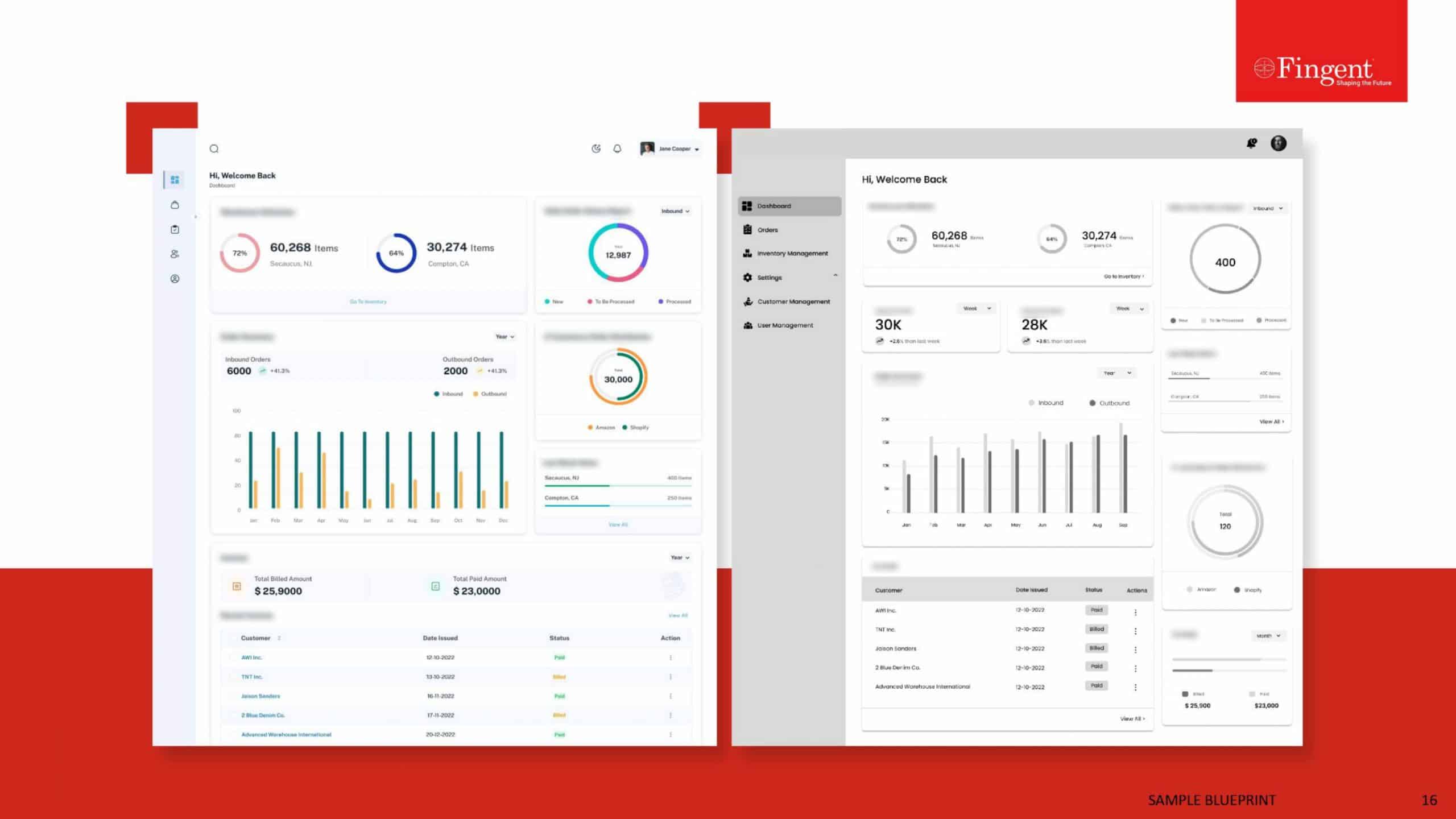
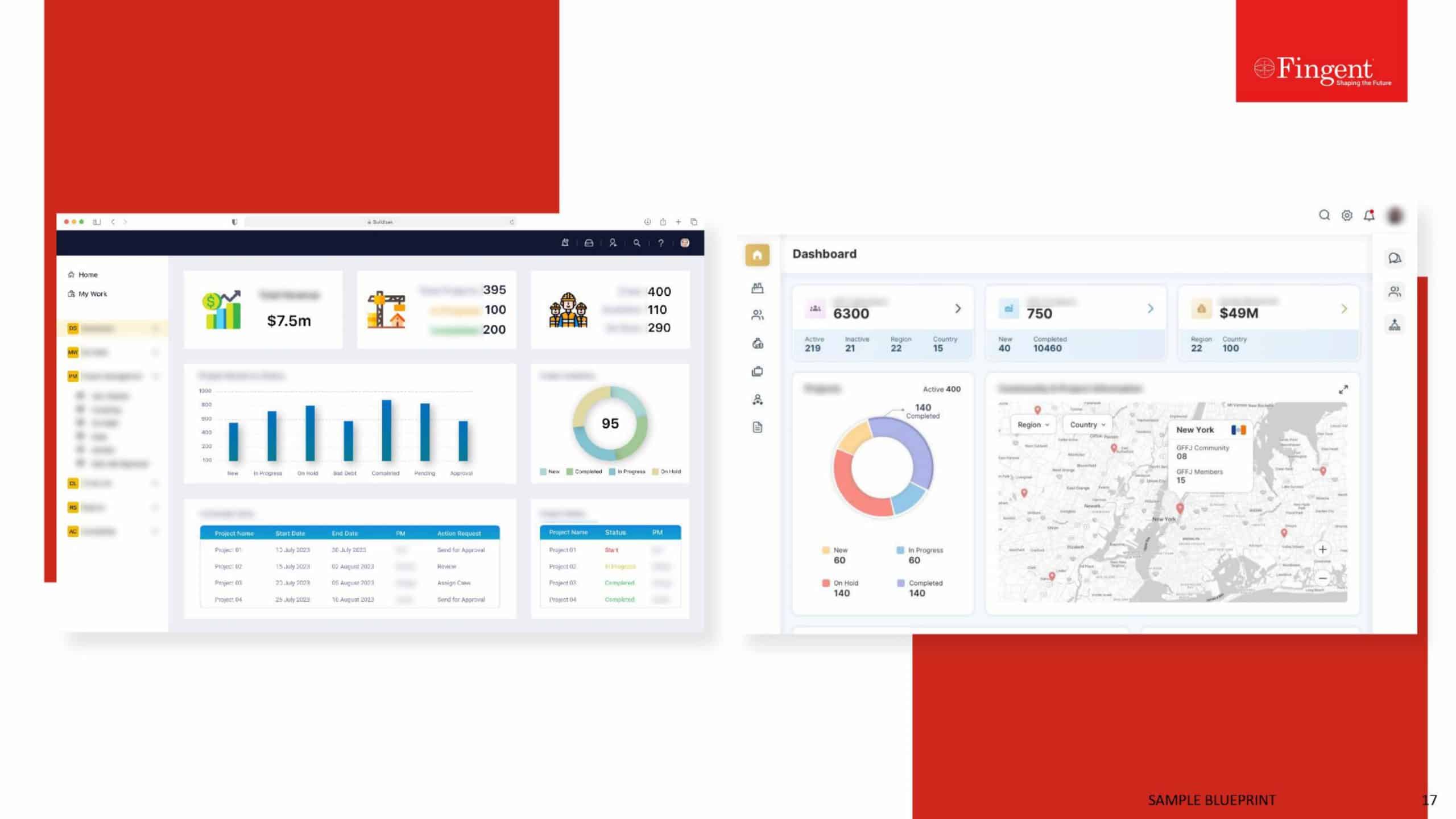
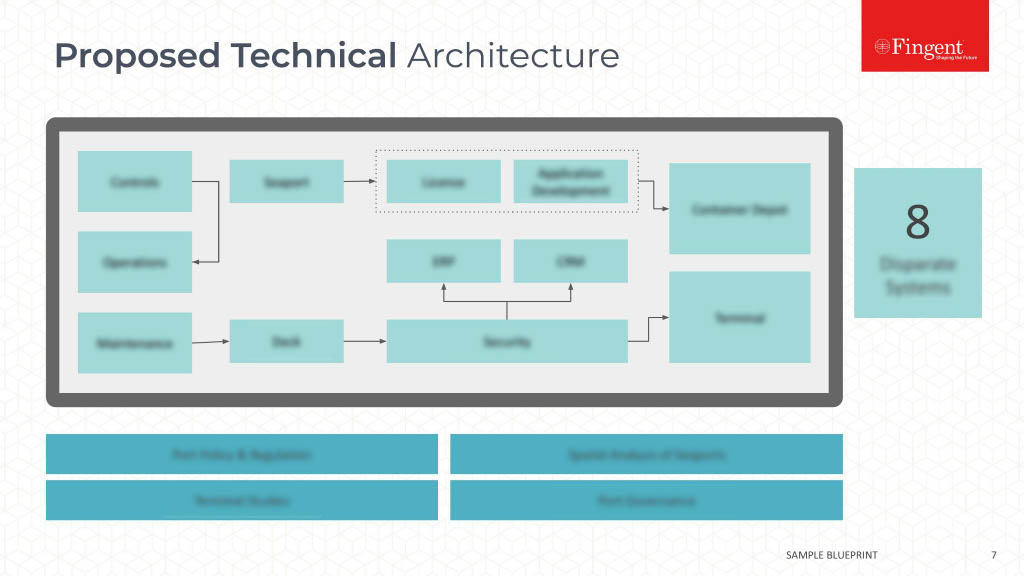
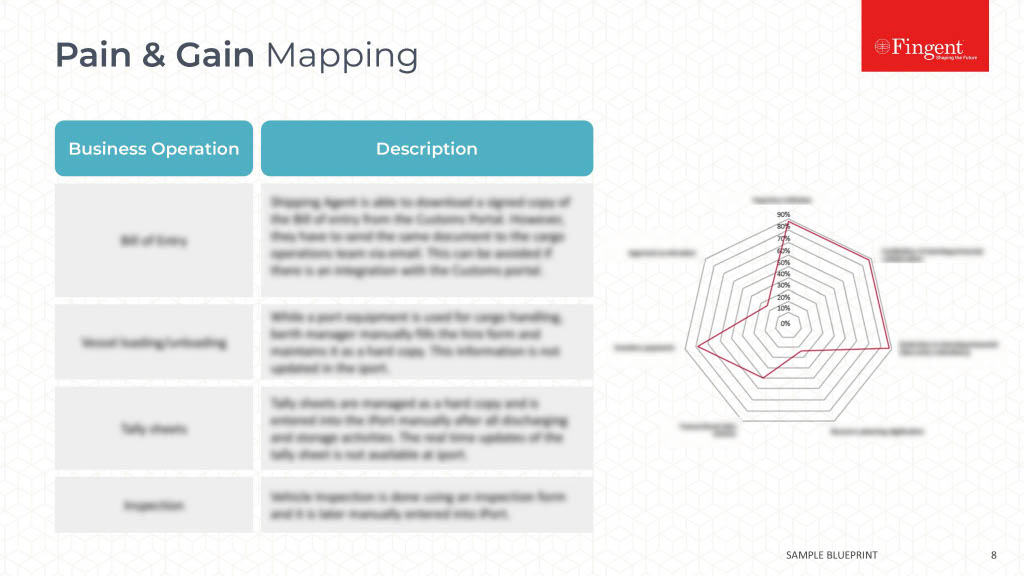
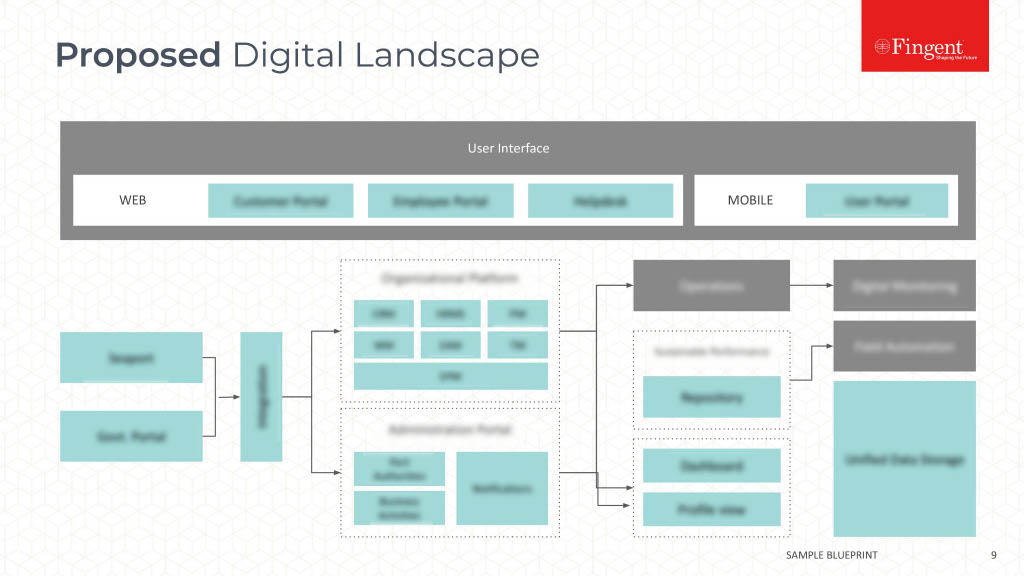
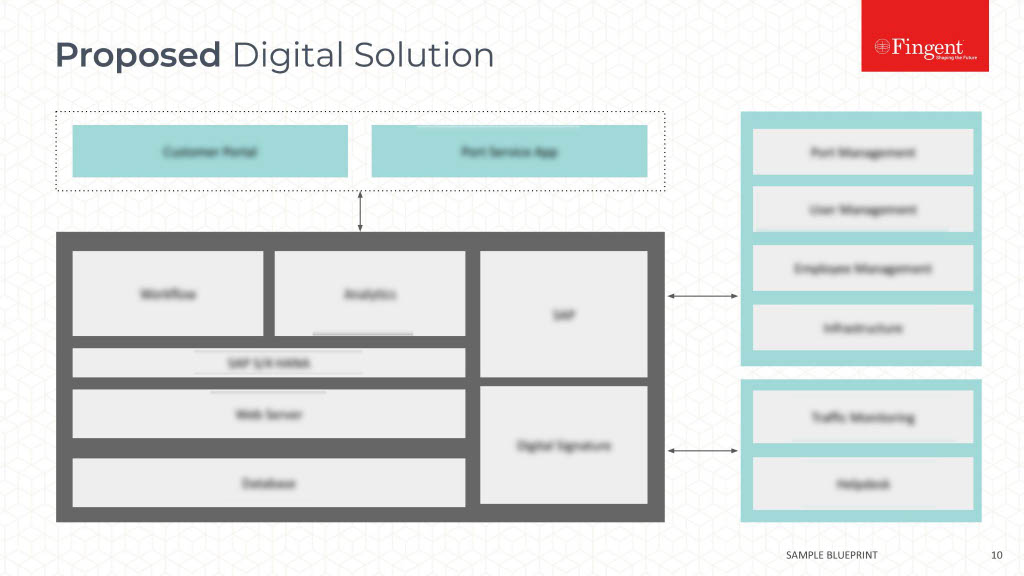
The Growing Significance of Health Information Technology

“Information is the lifeblood of medicine and health information technology is destined to be the circulatory system for that information.”
– David Blumenthal
What is Information Technology in Healthcare?
- Health information management across computing devices and platforms for hospitals, clinics, healthcare providers, and other medical centers
- Secure exchange of health information between consumers, providers, payers, insurers, and quality monitors
- Hardware and software solutions used to store, retrieve, share, and analyze healthcare information, medical data, and knowledge for seamless communication and decision-making
- Healthcare software used to manage daily clinical operations and administrative tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce costs and errors
- Remote/ virtual health monitoring and consulting solutions, medical mobile apps, online medical records, wearables, and self-management tools to facilitate personalized care
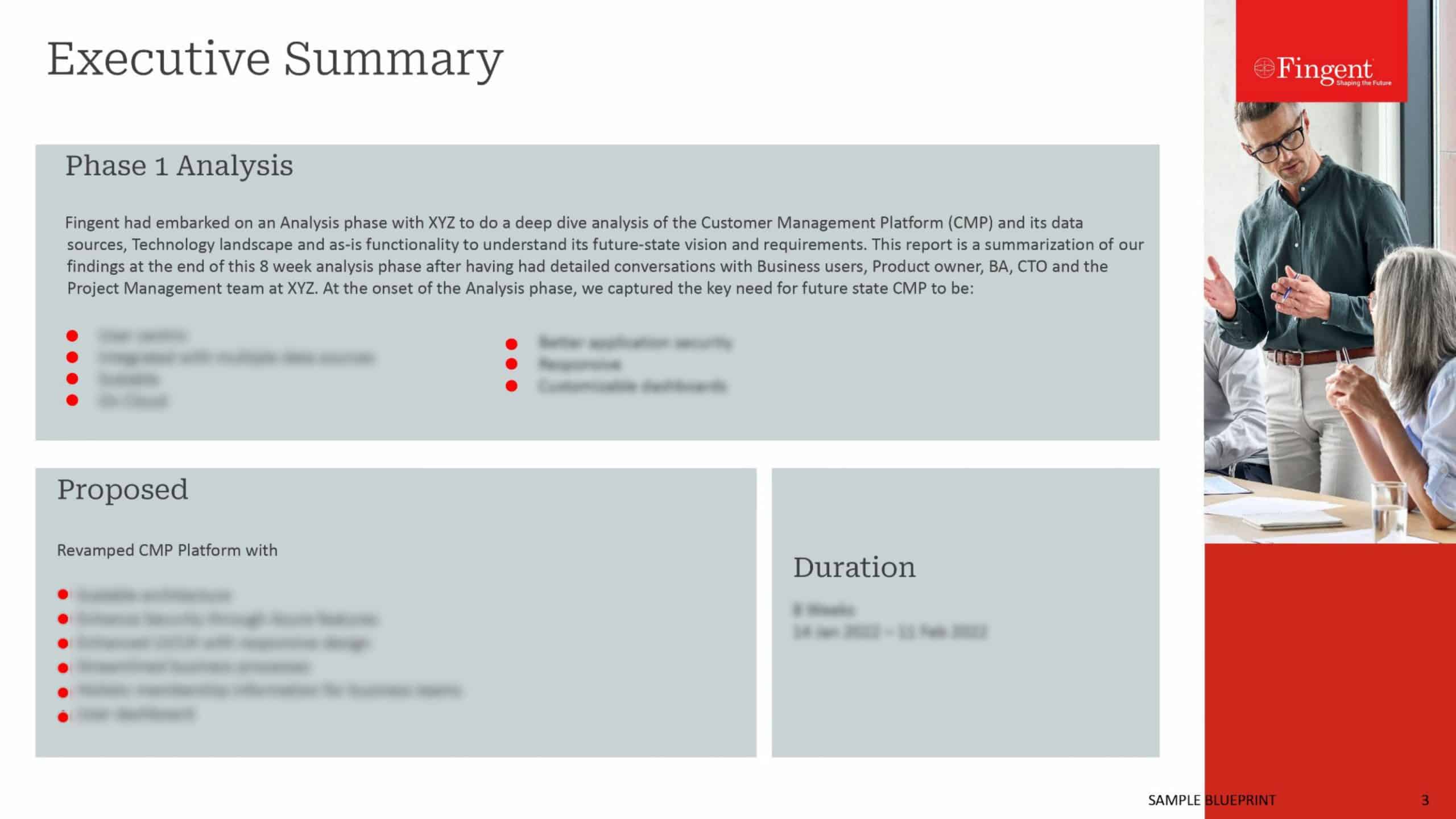
- Market size as of 2022: $394.6 billion
- Estimated value by 2027: $974.5 billion
- Projected Compound Annual Growth Rate: 19.8%
- Key market drivers: e-prescribing, telehealth, mHealth, and other HCIT solutions
Are you looking for custom software solutions tailored to healthcare needs?
Types of Health Information Technology
#1Electronic Health Records (EHR)
- Medical practitioners can quickly access a patient’s EMR using a mobile or computer
- Physicians can easily share data across different departments to provide quick and accurate treatment
- Digital creation and management of health records eliminate tedious paperwork and reduce the errors caused by manual documentation
- Easy to avoid medical errors since the same kind of health information is shared across all departments
#2Medical Practice Management Systems
- Automate routine clerical tasks such as scheduling appointments, billing & payment processing, claims administration, and other related procedures for managing your facility
- Streamline the workflow for doctors and clinical staff, so that they can spend more time with their patients and less time on administrative tasks
- Automate the process of stocking and distributing medical inventory and tracking the products dispensed to patients
- Generate detailed clinical performance reports to analyze the financial health of your medical practice and take the next steps to improve your cash flow
#3E-prescribing Software
- Eliminates the need to create handwritten notes by generating legible prescriptions online
- Avoids mix-up, loss, or misplacement of prescriptions and ensures the pharmacist supplies the right medicines to the patient
- Makes it easier to track a patient's medication history with the help of a pharmacy’s database
#4Remote Patient Monitoring Tools
- Glucometers for patients with diabetes
- IoT-based surveillance monitors to locate patients with critical conditions like dementia and alert healthcare professionals in case of an event like a fall
- Blood pressure monitors and heart rate monitors
- Post-operative cardiac monitoring devices for homecare
- Smart watches and wrist brands to track daily exercise routines and caloric intake
#5Medical Billing Software
- Facilitates proper information storage, reduces time-consuming paperwork, and increases convenience for the clinic staff and patients
- Streamlines clinical and administrative processes, improves staff productivity, and provides faster turnaround times for claims processing
- Improves overall clinical process efficiency by automating the steps involved in billing & invoicing, payment reminders, information management, claims, and reimbursements
Benefits of IT in the Healthcare Industry
- Provides healthcare professionals with accurate, actionable, and accessible information related to their patients’ health
- Facilitates enhanced communication and shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers
- Accurate maintenance and update of medical data and patient history across multiple platforms will reduce costly medical errors
- Up-to-date health information management ensures that every patient gets access to personalized care and treatment
- Enables faster and more informed decisions concerning health-related risks
- Healthcare applications provide easier access to explicit care guidelines and physician-recommended treatments
- Allows nursing professionals to focus more on the care they provide thereby reducing the chances for medical negligence
- Expands the collaboration between medical professionals by minimizing errors and miscommunication
- Better medication management and easier access for patients to their medical records
- Helps build social support networks for both patients as well as healthcare professionals
- Improves awareness among patients as well as the general public about health-related matters that can lead to positive outcomes
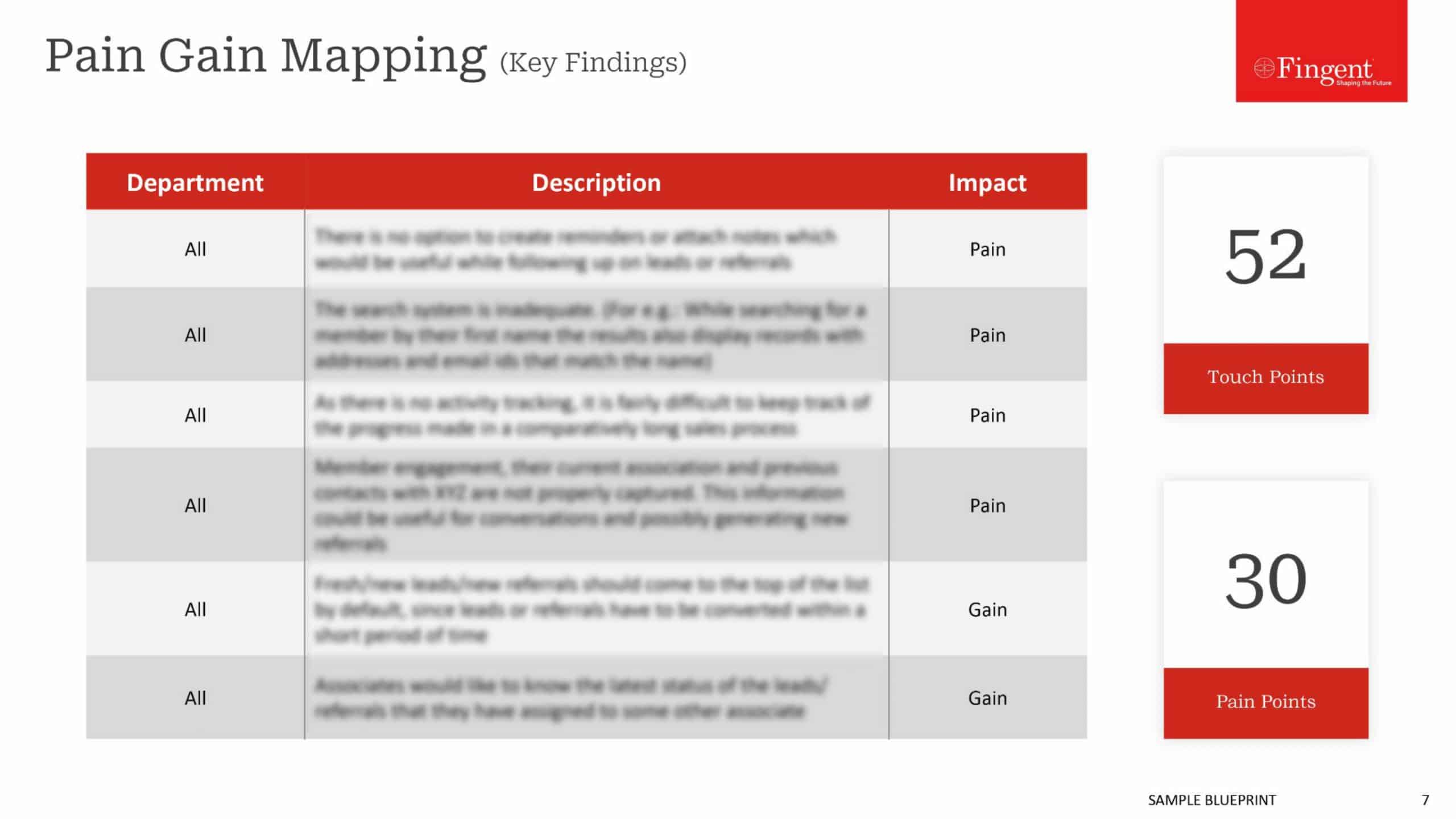
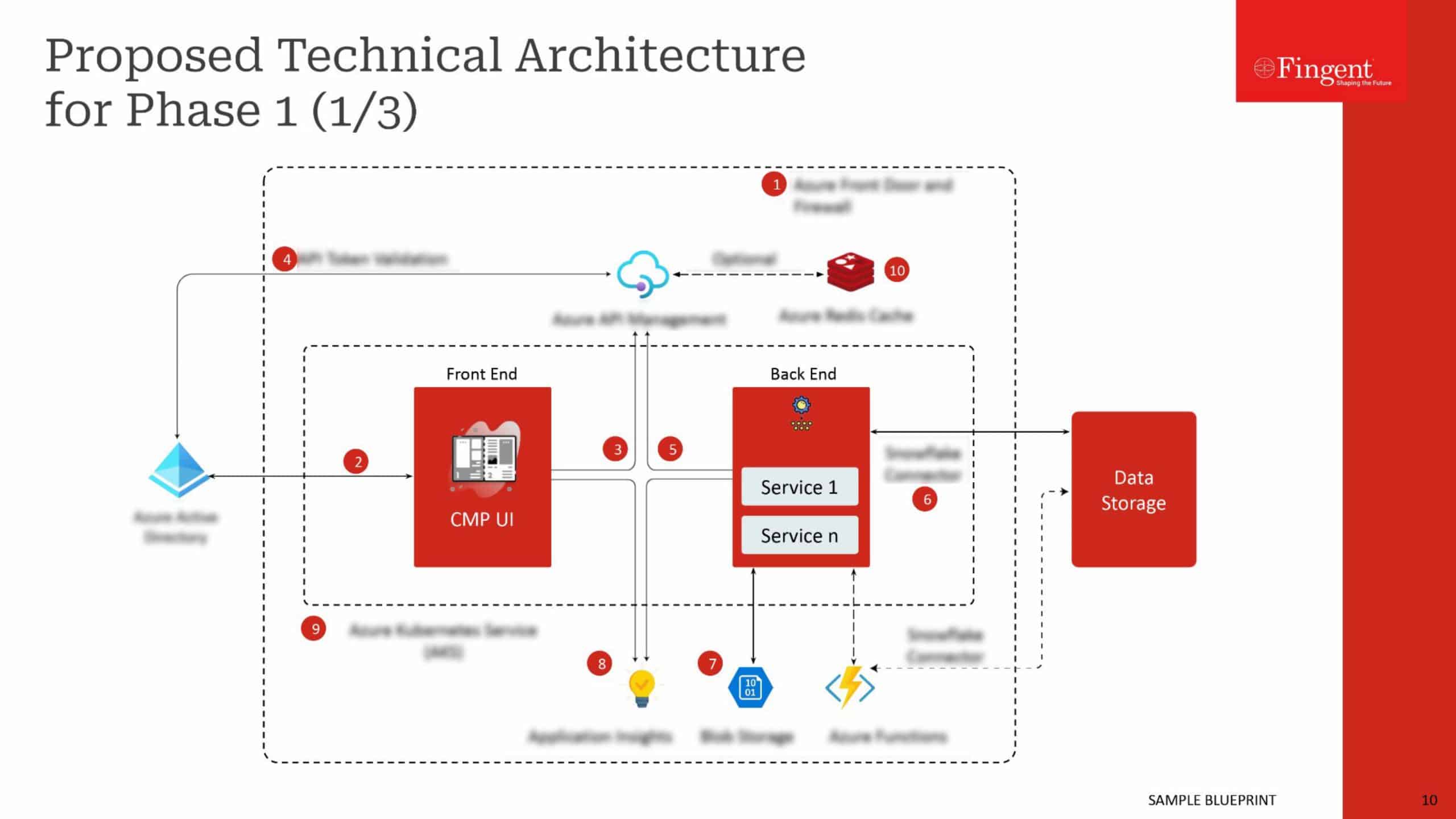
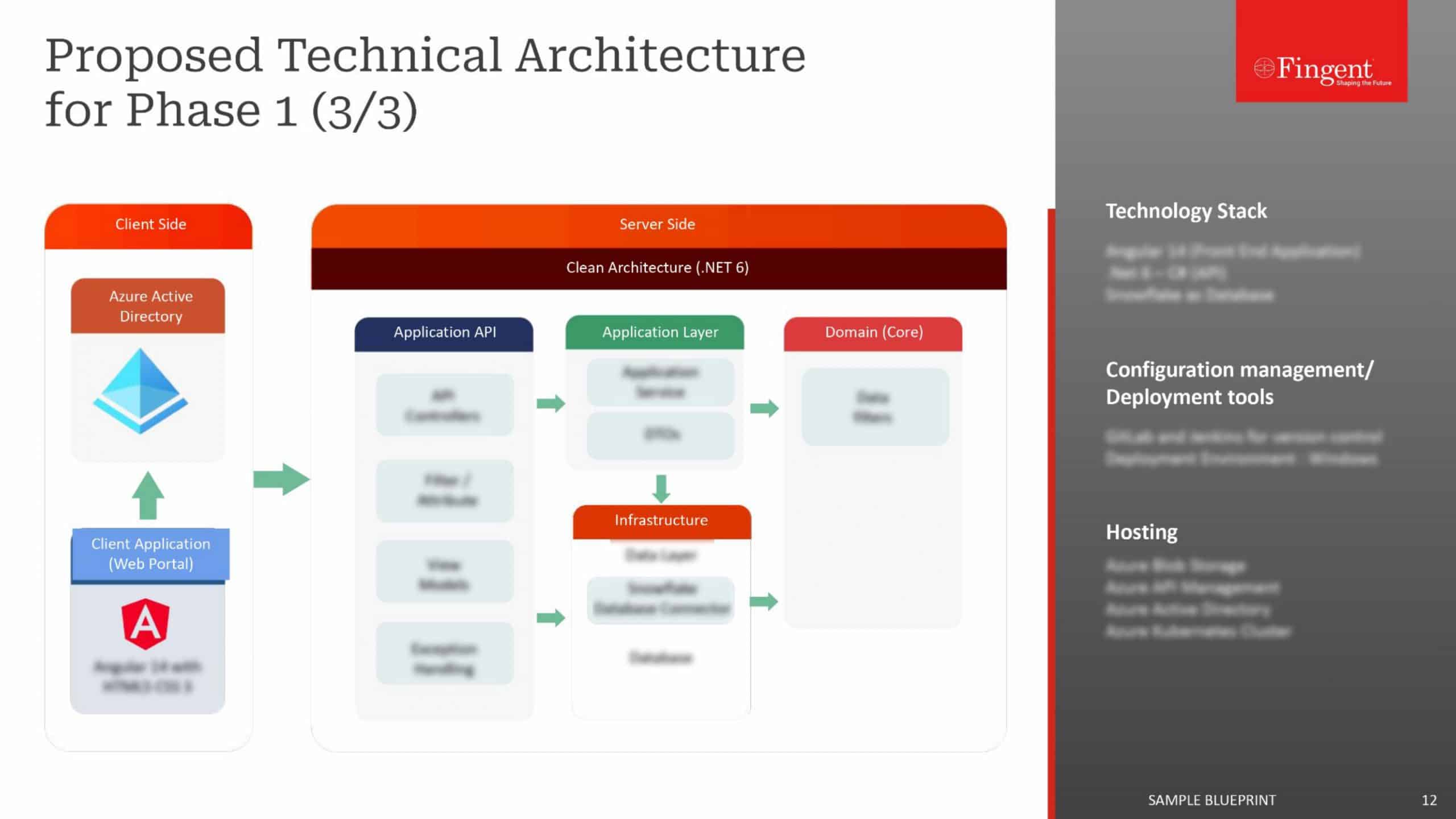
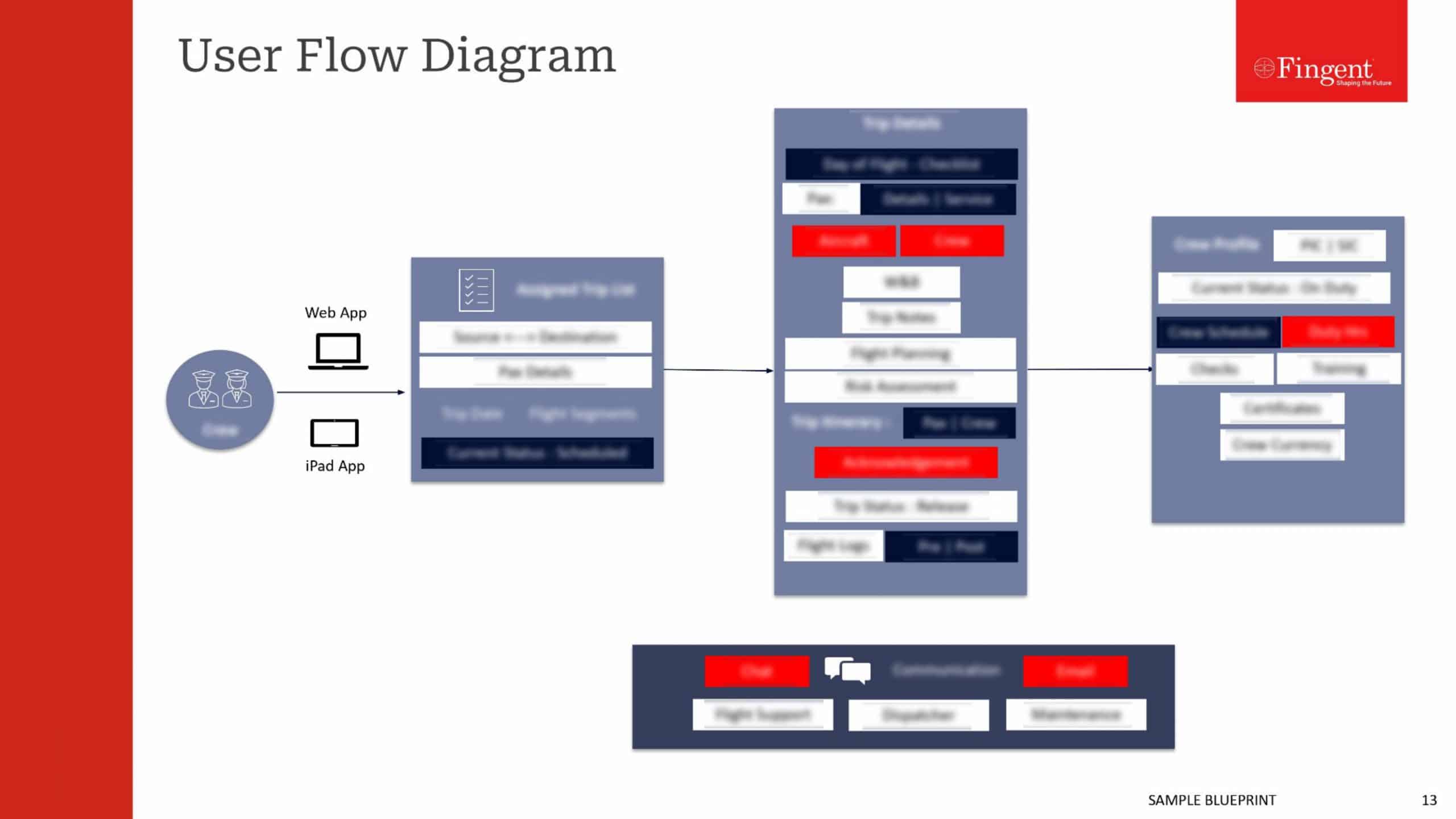
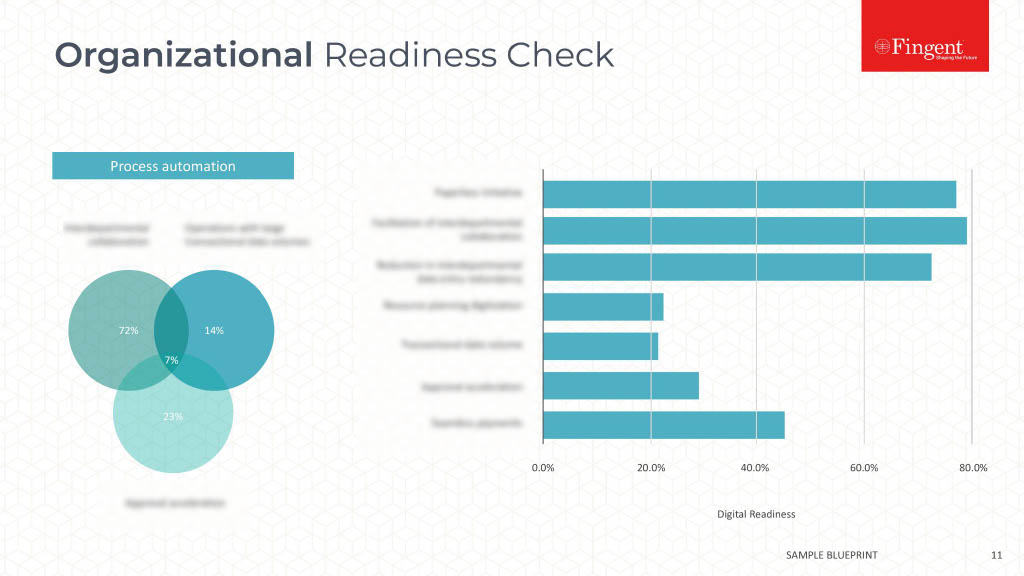
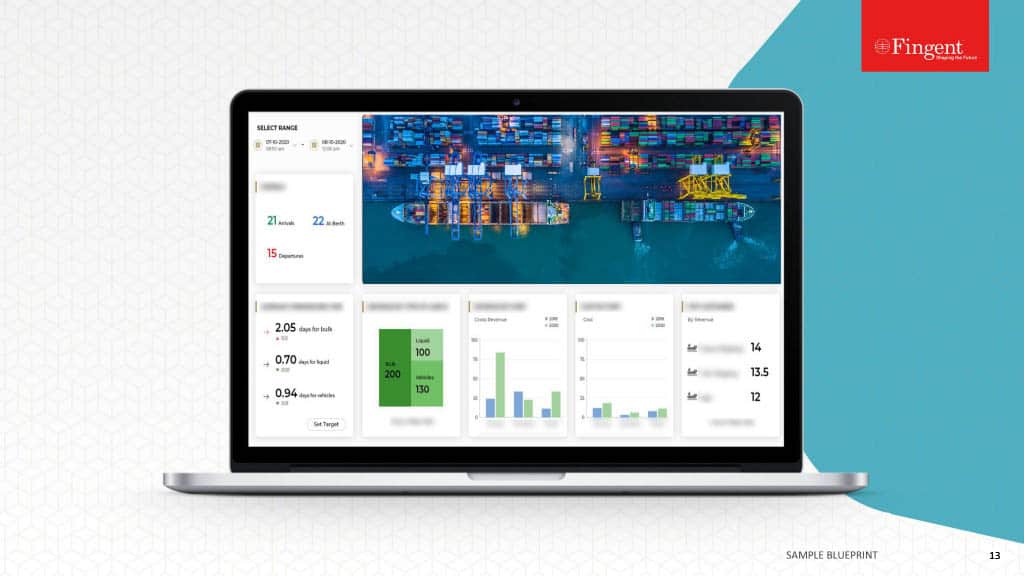
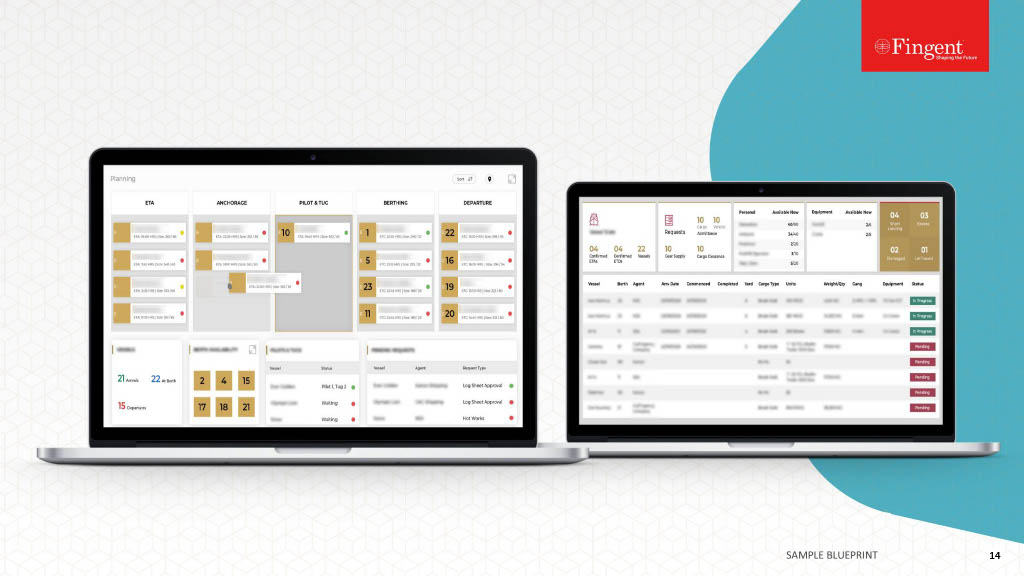
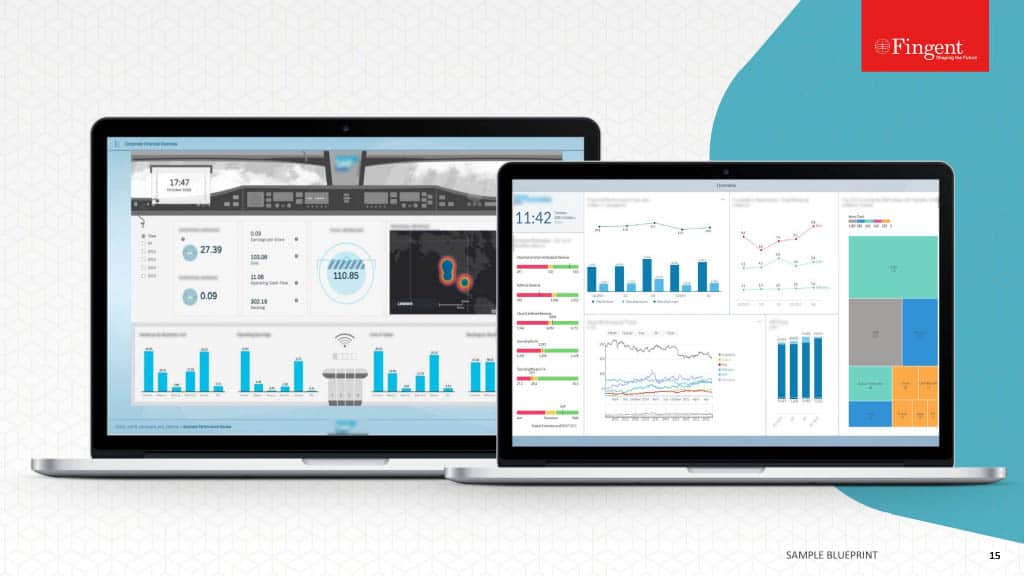
Web Application for Health Insurance Decision Makers: A Case Study
- Real-time insights and analytics empowered decision-makers to make well-informed choices.
- Enhanced focus on the specific requirements of healthcare payer organizations.
- A user-friendly interface enabled seamless data exploration and analysis.
- Substantial increase in new sales was achieved.
Know about the latest tech developments advancing in the healthcare industry.
Uses of Information Technology in Healthcare
Patient Records and Data Management
Digital management of patient data prevents important health information from getting lost, damaged, or misinterpreted. Health information technology applications enable healthcare professionals to manage patient data securely in a centralized location. A medical professional can add pharmacy records, X-rays, test results, and even vital signage to the virtual patient charts that are easy to read, share, analyze, and preserve for future reference.

Nursing Informatics
Nursing informatics is a fast-growing field in healthcare that combines patient care with data and technology to improve the quality of care, patient experience, and outcomes. In simple terms, nursing informatics specialists work with EHR systems and patient data management solutions to collect, analyze, optimize, and maintain patient data and build important reports for clinicians to make data-driven decisions.

Medical Data Collection and Research
Using health information technology applications such as EHRs, patient/ disease registries, discharge summaries, health surveys, and hospital databases, medical researchers can collect relevant data that will help them produce new medicines and design new types of treatments and conduct clinical trials. However, researchers gathering personal health information should obtain the required permission from data owners, adhere to data compliance regulations, and anonymize data samples before putting them into actual use.

Prevention and Control of Pandemic Epidemics
Digital health technologies play an important role in curbing the spread and impact of global pandemics like COVID-19. Health information technology aids in understanding the nature of diseases, improving diagnostic tools, and controlling the spread of infection on a larger scale. Telehealth systems, contact tracing apps, remote health monitoring tools, medical analytics, and online health surveys help control the spread of the infection, monitor outbreaks and their extent, and keep medical professionals and patients safe while providing continued care.

Monitor Patient Compliance
Remote patient monitoring tools, such as medical mobile apps, wearables, fitness apps, and custom healthcare applications for tracking conditions such as diabetes and oncology allow physicians to keep tabs on bed-ridden or homebound patients who need to be checked on more frequently. Instant feedback and suggestions from doctors enable the monitoring of patient compliance in real-time, especially by community pharmacists or home nurses who can make timely interventions to keep the patient safe and healthy.

Role of information technology in healthcare:
- Patient data management
- Health information exchange
- Reduce medical errors
- Protect patient privacy
- Enhance clinical decision-making
- Validate and process insurance claims
- Improve patient care and experience
- Ensure accuracy in test reports and diagnosis
- Prevent adverse drug reactions
Top Health Information Technology Trends
#1Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- Devices and networks that enable telemedicine and virtual care
- Remote patient monitoring devices to observe patients with chronic conditions in their homes
- Wearable or on-body IoMT devices that are connected to a person's body and record medical information about them, such as heart rate or blood pressure
- Glucose monitoring and calorie intake tracking mobile apps on patients’ smartphones
#2Virtual Reality
- 3D models and simulated virtual environments for anatomy learning and improving medical social skills
- Simulation of medical procedures, emergency cases, and medical equipment training
- Practice and train surgeons by conducting mock-surgeries in a virtual operating room
- Immersive VR simulations and gamified experiences for patients to alleviate chronic pains as well as mental stress and anxiety
- Inspiring and engaging VR-powered sessions to aid physical therapies and exercises as well as cognitive and neuro rehabilitation
#3Augmented Reality
- AR-enabled virtualized training provides medical practitioners with deeper insights into the nuances of body functions
- AR-based data visualization tools enable medical R&D teams to expedite the study of genetic data related to specific microbes
- AR helps create digital models of complicated surgeries including multiple sub-steps and critical deviations requiring careful analysis and planning
- 3D medical imaging, real-time access of patient data from EMRs, precise symptom detection, and collaborative surgeries
- Operating suite preparation, accurate vein visualization on the patient’s arm, dental learning and practice, and immersive medical training
#4Artificial Intelligence
- AI in medical diagnostics helps unlock massive amounts of clinical data to boost medical diagnosis
- Allows doctors and caregivers to detect potentially life-threatening ailments at more treatable stages
- Reduces diagnostic errors and suggests the best practices for post-surgical care, patient discharge, medications, and follow-up checks
- Helps streamline drug research and discovery, and reduces the time-to-market for new drugs
- AI algorithms run behind self-health monitoring devices such as wearables, activity trackers, pedometers, smartwatches, and other physical fitness monitoring gadgets to derive in-depth insights on patient health
#5Cloud Adoption in Healthcare
- Unified view of patient profile and records by pulling together data from different hospital systems
- Facilitates collaborative decision-making by integrating data across the care continuum
- Fosters remote collaboration between healthcare providers, care systems, staff, and patients
- Healthcare leaders can unlock the value of data generated along the patient journey, from the hospital to the home
- Flexibility for healthcare providers to scale up or down as demands evolve, without being locked into fixed capital expenses or investing in new systems
Are You Looking For Industry Experts To Build Your Software?
Key Considerations for Implementing Information Technology in Healthcare
- Identify existing problems as well as areas for improvement in your healthcare practice or organization.
- Find out if the health information technology you’re considering is capable of tackling the problem.
- Involve and get the buy-in of different professional stakeholder groups, such as doctors, nurses, clinical and administrative staff, managers, senior management, and other strategic leaders in your organization.
- Commit adequate time and resources to define your business case, evaluate various HIT providers, contact their references, and review the healthcare technology solutions they’ve built in the past.
- Decide whether you need an off-the-shelf standardized solution or a home-grown customized healthcare software. While commercial systems may appear cheaper to purchase, they are not customized to individual organizations, which will increase your future overheads.
- It’s always advisable to build a customized healthcare system for your organization that will fulfill a range of requirements on a variety of levels. Tailor-made healthcare software systems ensure a careful balance between affordability and desired functionality.
- Decide how to prioritize the implementation of functionality that can bring benefits to the maximum number of end-users at the earliest stage itself.
- Focus on developing the right infrastructure for your healthcare technology application in order to ensure improved usability and performance.
- Implement software training programs tailored to individual roles of users, so they get adapted to the new system quickly.
- Continuously evaluate the progress of technology adoption, capture user feedback about problems that are identified, and respond to it in a timely manner.
- Maintain your healthcare software with regular system re-visits, scheduled software maintenance, patches and updates, and system upgrades to ensure optimal performance round-the-clock.
How Can Fingent Help?
Frequently Asked Questions About Health Information Technology
- >> gain end-to-end visibility over your routine clinical activities,
- >> integrate disparate applications used for different purposes,
- >> generate custom reports,
- >> get up-to-date medical data across all your devices and applications,
- >> reduce total cost of ownership,
- >> ensure health information safety,
- >> track medical history of patients,
- >> optimize revenue, and gain financial stability.